Page 116 - Read Online
P. 116
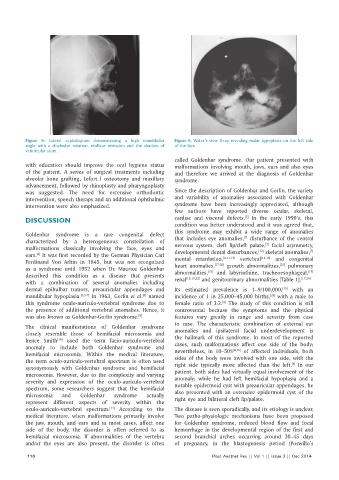
Figure 5: Lateral cephalogram demonstrating a high mandibular Figure 6: Water’s view X-ray revealing malar hypoplasia on the left side
angle with a clockwise rotation, midface retrusion and the shadow of of the face
ventricular stunt
called Goldenhar syndrome. Our patient presented with
with education should improve the oral hygiene status malformations involving mouth, jaws, ears and also eyes
of the patient. A series of surgical treatments including and therefore we arrived at the diagnosis of Goldenhar
alveolar bone grafting, Lefort I osteotomy and maxillary syndrome.
advancement, followed by rhinoplasty and pharyngoplasty
was suggested. The need for extensive orthodontic Since the description of Goldenhar and Gorlin, the variety
intervention, speech therapy and an additional ophthalmic and variability of anomalies associated with Goldenhar
intervention were also emphasized. syndrome have been increasingly appreciated, although
few authors have reported diverse ocular, skeletal,
[7]
DISCUSSION cardiac and visceral defects. In the early 1990’s, this
condition was better understood and it was agreed that,
this syndrome may exhibit a wide range of anomalies
Goldenhar syndrome is a rare congenital defect [7]
characterized by a heterogeneous constellation of that includes eye anomalies, disturbance of the central
[7]
malformations classically involving the face, eyes and nervous system, cleft lip/cleft palate, facial asymmetry,
[7]
[12]
ears. It was first recorded by the German Physician Carl developmental dental disturbances, skeletal anomalies,
[4]
vertebral
mental retardation,
[14-16]
and congenital
[4,11,13]
Ferdinand Von Arltin in 1845, but was not recognized heart anomalies, [17-20] growth abnormalities, pulmonary
[21]
as a syndrome until 1952 when Dr. Maurice Goldenhar abnormalities, and labyrinthine, tracheoesophageal,
[15]
[15]
described this condition as a disease that presents renal [15,16,22] and genitourinary abnormalities [Table 1]. [17,20]
with a combination of several anomalies including
dermal epibulbar tumors, preauricular appendages and Its estimated prevalence is 1–9/100,000, with an
[13]
mandibular hypoplasia. [3,5-7] In 1963, Gorlin et al. named incidence of 1 in 25,000–45,000 births, with a male to
[28]
[8]
this syndrome oculo-auriculo-vertebral syndrome due to female ratio of 3:2. The study of this condition is still
[4]
the presence of additional vertebral anomalies. Hence, it controversial because the symptoms and the physical
was also known as Goldenhar-Gorlin syndrome. [9] features vary greatly in range and severity from case
to case. The characteristic combination of external ear
The clinical manifestations of Goldenhar syndrome
closely resemble those of hemifacial microsomia and anomalies and ipsilateral facial underdevelopment is
hence Smith used the term facio-auriculo-vertebral the hallmark of this syndrome. In most of the reported
[10]
anomaly to include both Goldenhar syndrome and cases, such malformations affect one side of the body;
[4,16]
hemifacial microsomia. Within the medical literature, nevertheless, in 10–50% of affected individuals, both
the term oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum is often used sides of the body were involved with one side, with the
[4]
synonymously with Goldenhar syndrome and hemifacial right side typically more affected than the left. In our
microsomia. However, due to the complexity and varying patient, both sides had virtually equal involvement of the
severity and expression of the oculo-auriculo-vertebral anomaly; while he had left hemifacial hypoplasia and a
notable epidermoid cyst with preauricular appendages, he
spectrum, some researchers suggest that the hemifacial also presented with an extensive epidermoid cyst of the
microsomia and Goldenhar syndrome actually right eye and bilateral cleft lip/palate.
represent different aspects of severity within the
oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum. According to the The disease is seen sporadically, and its etiology is unclear.
[11]
medical literature, when malformations primarily involve Two patho-physiologic mechanisms have been proposed
the jaw, mouth, and ears and in most cases, affect one for Goldenhar syndrome, reduced blood flow and focal
side of the body, the disorder is often referred to as hemorrhage in the developmental region of the first and
hemifacial microsomia. If abnormalities of the vertebra second branchial arches occurring around 30–45 days
and/or the eyes are also present, the disorder is often of pregnancy, in the blastogenesis period (Poswillo’s
110 Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 1 || Issue 3 || Dec 2014