Page 115 - Read Online
P. 115
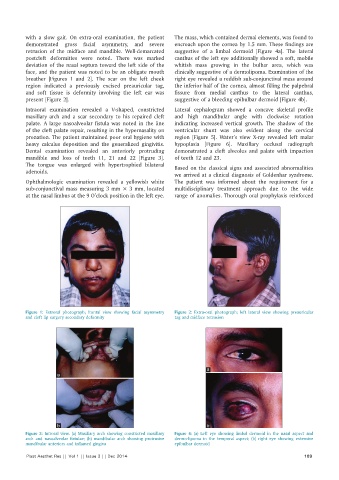
with a slow gait. On extra-oral examination, the patient The mass, which contained dermal elements, was found to
demonstrated gross facial asymmetry, and severe encroach upon the cornea by 1.5 mm. These findings are
retrusion of the midface and mandible. Well-demarcated suggestive of a limbal dermoid [Figure 4a]. The lateral
postcleft deformities were noted. There was marked canthus of the left eye additionally showed a soft, mobile
deviation of the nasal septum toward the left side of the whitish mass growing in the bulbar area, which was
face, and the patient was noted to be an obligate mouth clinically suggestive of a dermolipoma. Examination of the
breather [Figures 1 and 2]. The scar on the left cheek right eye revealed a reddish sub-conjunctival mass around
region indicated a previously excised preauricular tag, the inferior half of the cornea, almost filling the palpebral
and soft tissue is deformity involving the left ear was fissure from medial canthus to the lateral canthus,
present [Figure 2]. suggestive of a bleeding epibulbar dermoid [Figure 4b].
Intraoral examination revealed a V-shaped, constricted Lateral cephalogram showed a concave skeletal profile
maxillary arch and a scar secondary to his repaired cleft and high mandibular angle with clockwise rotation
palate. A large nasoalveolar fistula was noted in the line indicating increased vertical growth. The shadow of the
of the cleft palate repair, resulting in the hypernasality on ventricular shunt was also evident along the cervical
pronation. The patient maintained poor oral hygiene with region [Figure 5]. Water’s view X-ray revealed left malar
heavy calculus deposition and the generalized gingivitis. hypoplasia [Figure 6]. Maxillary occlusal radiograph
Dental examination revealed an anteriorly protruding demonstrated a cleft alveolus and palate with impaction
mandible and loss of teeth 11, 21 and 22 [Figure 3]. of teeth 12 and 23.
The tongue was enlarged with hypertrophied bilateral Based on the classical signs and associated abnormalities
adenoids.
we arrived at a clinical diagnosis of Goldenhar syndrome.
Ophthalmologic examination revealed a yellowish white The patient was informed about the requirement for a
sub-conjunctival mass measuring 3 mm × 3 mm, located multidisciplinary treatment approach due to the wide
at the nasal limbus at the 9 O’clock position in the left eye. range of anomalies. Thorough oral prophylaxis reinforced
Figure 1: Extroral photograph; frontal view showing facial asymmetry Figure 2: Extra-oral photograph; left lateral view showing preauricular
and cleft lip surgery secondary deformity tag and midface retrusion
a
a
b b
Figure 3: Introral view. (a) Maxillary arch showing constricted maxillary Figure 4: (a) Left eye showing limbal dermoid in the nasal aspect and
arch and nasoalveolar fistulae; (b) mandibular arch showing protrusive dermo-lipoma in the temporal aspect; (b) right eye showing extensive
mandibular anteriors and inflamed gingiva epibulbar dermoid
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 1 || Issue 3 || Dec 2014 109