Page 121 - Read Online
P. 121
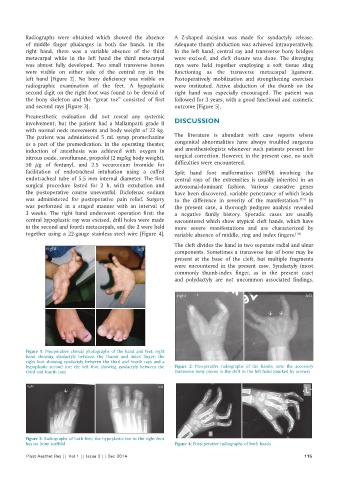
Radiographs were obtained which showed the absence A Z-shaped incision was made for syndactyly release.
of middle finger phalanges in both the hands. In the Adequate thumb abduction was achieved intraoperatively.
right hand, there was a variable absence of the third In the left hand, central ray and transverse bony bridges
metacarpal while in the left hand the third metacarpal were excised, and cleft closure was done. The diverging
was almost fully developed. Two small transverse bones rays were held together employing a soft tissue sling
were visible on either side of the central ray in the functioning as the transverse metacarpal ligament.
left hand [Figure 2]. No bony deficiency was visible on Postoperatively mobilization and strengthening exercises
radiographic examination of the feet. A hypoplastic were instituted. Active abduction of the thumb on the
second digit on the right foot was found to be devoid of right hand was especially encouraged. The patient was
the bony skeleton and the “great toe” consisted of first followed for 3 years, with a good functional and cosmetic
and second rays [Figure 3]. outcome [Figure 5].
Preanesthetic evaluation did not reveal any systemic
involvement, but the patient had a Mallampatti grade II DISCUSSION
with normal neck movements and body weight of 22 kg.
The patient was administered 5 mL syrup promethazine The literature is abundant with case reports where
as a part of the premedication. In the operating theater, congenital abnormalities have always troubled surgeons
induction of anesthesia was achieved with oxygen in and anesthesiologists whenever such patients present for
nitrous oxide, sevoflurane, propofol (2 mg/kg body weight), surgical correction. However, in the present case, no such
50 μg of fentanyl, and 2.5 vecuronium bromide for difficulties were encountered.
facilitation of endotracheal intubation using a cuffed Split hand foot malformation (SHFM) involving the
endotracheal tube of 5.5 mm internal diameter. The first central rays of the extremities is usually inherited in an
surgical procedure lasted for 2 h, with extubation and autosomal-dominant fashion. Various causative genes
the postoperative course uneventful. Diclofenac sodium have been discovered, variable penetrance of which leads
was administered for postoperative pain relief. Surgery to the difference in severity of the manifestation. [7-9] In
was performed in a staged manner with an interval of the present case, a thorough pedigree analysis revealed
3 weeks. The right hand underwent operation first: the a negative family history. Sporadic cases are usually
central hypoplastic ray was excised, drill holes were made encountered which show atypical cleft hands, which have
in the second and fourth metacarpals, and the 2 were held more severe manifestations and are characterized by
together using a 22-gauge stainless steel wire [Figure 4]. variable absence of middle, ring and index fingers. [10]
The cleft divides the hand in two separate radial and ulnar
components. Sometimes a transverse bar of bone may be
present at the base of the cleft, but multiple fragments
were encountered in the present case. Syndactyly (most
commonly thumb-index finger, as in the present case)
and polydactyly are not uncommon associated findings.
Figure 1: Preoperative clinical photographs of the hand and feet; right
hand showing syndactyly between the thumb and index finger; the
right foot showing syndactyly between the third and fourth rays and a
hypoplastic second toe; the left foot showing syndactyly between the Figure 2: Preoperative radiographs of the hands; note the accessory
third and fourth toes transverse bony pieces in the cleft in the left hand (marked by arrows)
Figure 3: Radiographs of both feet; the hypoplastic toe in the right foot
has no bony scaffold Figure 4: Postoperative radiographs of both hands
Plast Aesthet Res || Vol 1 || Issue 3 || Dec 2014 115