Page 59 - Read Online
P. 59
Yaroustovsky et al. Blood purification in intensive care patients
We have shown the successful use of CVVHF in rate of 20-40 mL/kg/h to ensure the required quality of
conjunction with ECMO in children (more than 80 the procedure. Anticoagulation was carried out for the
patients) who have undergone correction of complex combined ECMO and HF single circuit with the use of
congenital heart defects. This combination of unfractionated heparin; the activated clotting time was
[20]
different techniques in a single extracorporeal maintained within 180-200 s.
circuit allows the correction of water and electrolyte
disturbances, metabolic disorders and azotemia from The circuit lifetime should not exceed 48 h. Since the
the first day of treatment. Moreover, the prescribed aim of the CVVHF connection was to perform RRT, its
ultrafiltration volume is calculated and programmed duration was determined by the dynamics of the renal
according to the level of volemia in each specific dysfunction and the clinical state of the child.
case. The determining factors are as follows: CVP
and Pla, pulmonary artery pressure, ventricular end- The use of methods of extracorporeal blood purification
diastolic volumes, the volume of necessary infusion should be considered a “bridge” to the recovery of
and transfusion therapy and nutritional support. Only kidney function. Given the obvious need to control the
one day after connecting CVVHF to an ECMO circuit, electrolyte, acid-base and water balance in patients
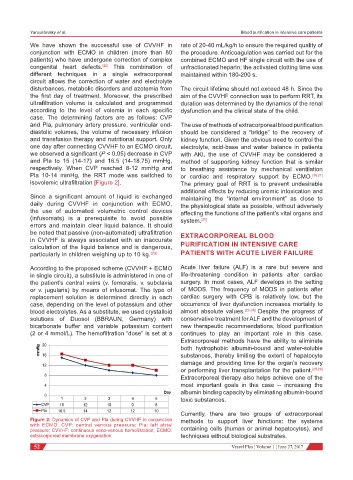
we observed a significant (P < 0.05) decrease in CVP with AKI, the use of CVVHF may be considered a
and Pla to 15 (14-17) and 16.5 (14-18.75) mmHg, method of supporting kidney function that is similar
respectively. When CVP reached 8-12 mmHg and to breathing assistance by mechanical ventilation
Pla 10-14 mmHg, the RRT mode was switched to or cardiac and respiratory support by ECMO. [19,21]
isovolemic ultrafiltration [Figure 2]. The primary goal of RRT is to prevent undesirable
additional effects by reducing uremic intoxication and
Since a significant amount of liquid is exchanged maintaining the “internal environment” as close to
daily during CVVHF in conjunction with ECMO, the physiological state as possible, without adversely
the use of automated volumetric control devices affecting the functions of the patient’s vital organs and
(infusomats) is a prerequisite to avoid possible system. [20]
errors and maintain clear liquid balance. It should
be noted that passive (non-automated) ultrafiltration EXTRACORPOREAL BLOOD
in CVVHF is always associated with an inaccurate
calculation of the liquid balance and is dangerous, PURIFICATION IN INTENSIVE CARE
particularly in children weighing up to 10 kg. [20] PATIENTS WITH ACUTE LIVER FAILURE
According to the proposed scheme (CVVHF + ECMO Acute liver failure (ALF) is a rare but severe and
in single circuit), a substitute is administered in one of life-threatening condition in patients after cardiac
the patient’s central veins (v. femoralis, v. subclavia surgery. In most cases, ALF develops in the setting
or v. jugularis) by means of infusomat. The type of of MODS. The frequency of MODS in patients after
replacement solution is determined directly in each cardiac surgery with CPB is relatively low, but the
case, depending on the level of potassium and other occurrence of liver dysfunction increases mortality to
blood electrolytes. As a substitute, we used crystalloid almost absolute values. [22-24] Despite the progress of
solutions of Duosol (BBRAUN, Germany) with conservative treatment for ALF and the development of
bicarbonate buffer and variable potassium content new therapeutic recommendations, blood purification
(2 or 4 mmol/L). The hemofiltration “dose” is set at a continues to play an important role in this case.
Extracorporeal methods have the ability to eliminate
both hydrophobic albumin-bound and water-soluble
substances, thereby limiting the extent of hepatocyte
damage and providing time for the organ’s recovery
or performing liver transplantation for the patient. [25,26]
Extracorporeal therapy also helps achieve one of the
most important goals in this case -- increasing the
albumin binding capacity by eliminating albumin-bound
toxic substances.
Currently, there are two groups of extracorporeal
Figure 2: Dynamics of CVP and Pla during CVVHF in conjunction methods to support liver functions: the systems
with ECMO. CVP: central venous pressure; Pla: left atrial
pressure; CVVHF: continuous veno-venous hemofiltration; ECMO: containing cells (human or animal hepatocytes), and
extracorporeal membrane oxygenation techniques without biological substrates.
52 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 27, 2017