Page 61 - Read Online
P. 61
Yaroustovsky et al. Blood purification in intensive care patients
Extracorporeal liver support provided a statistically above 30, a statistically significant increase in survival
significant reduction in total bilirubin concentration rate was found. Taking such results into account,
[45]
(8.6% for MARS-therapy (P = 0.028) and 33% for we recommend to perform a differentiated evaluation
Prometheus (P < 0.001)). Prometheus-therapy of extracorporeal therapy effectiveness, including its
also provided significant clearance of unconjugated effect on survival rate in specific patient subgroups.
bilirubin (29%, P = 0.003). [39] These results agree with
data from other researchers, who reported a total At the A.N. Bakulev NSPCCS, the MARS-therapy
bilirubin reduction of 26-59% during Prometheus and method was successfully applied for the first time
of 23% during albumin dialysis. [41-43] Such differences in children with MODS after the radical correction
in reducing the level of total bilirubin are primarily due of congenital heart disease. Patients with MODS
to the technical characteristics of the membranes and developed severe hepatic failure along with heart (EF
the different rates of perfusion and albumin dialysate/ < 40%, required inotropic support), respiratory and
plasma. renal failure. We observed the failure of conservative
therapy for hepatic insufficiency, progressive increases
During our study, we noted positive dynamics of in bilirubin (up to 500 μmol/L) and cytolytic syndrome
the serum aminotransferase levels, which reflect with an increase of ASAT and ALAT enzymes (more
hepatocyte cytolysis. This trend indirectly indicated than 200 U/L). During MARS-therapy, positive
a decrease in the degree of liver parenchyma lesion. dynamics were more evident in children than in adults.
The decrease of ASAT and ALAT was 15.5% (P The reduction of jaundice was noted at the end of the
= 1.0) and 43% (P = 0.31) during MARS-therapy, procedure (duration: 16-18 h), which indicates the
respectively, and 8% (P = 0.79) and 26% (P = 0.0005) effective elimination of bilirubin and bile acids. This
during Prometheus-therapy, respectively. According fact can be explained by the ratio of the child’s body
to foreign colleagues, Prometheus-therapy decreases surface area to the sorption capacity of the columns
serum aminotransferase to 40-55% in patients with with activated carbon and ion-exchange resin.
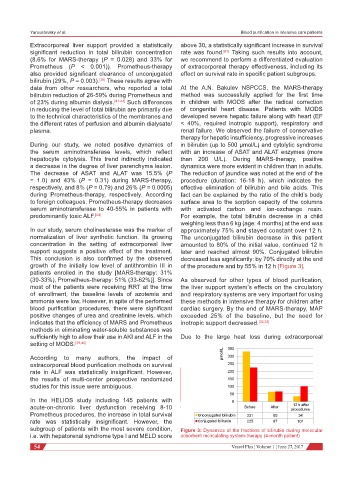
predominantly toxic ALF. [44] For example, the total bilirubin decrease in a child
weighing less than 6 kg (age: 4 months) at the end was
In our study, serum cholinesterase was the marker of approximately 75% and stayed constant over 12 h.
normalization of liver synthetic function. Its growing The unconjugated bilirubin decrease in this patient
concentration in the setting of extracorporeal liver amounted to 80% of the initial value, continued 12 h
support suggests a positive effect of the treatment. later and reached almost 90%. Conjugated bilirubin
This conclusion is also confirmed by the observed decreased less significantly: by 70% directly at the end
growth of the initially low level of antithrombin III in of the procedure and by 55% in 12 h [Figure 3].
patients enrolled in the study [MARS-therapy: 31%
(30-33%), Prometheus-therapy: 51% (33-62%)]. Since As observed for other types of blood purification,
most of the patients were receiving RRT at the time the liver support system’s effects on the circulatory
of enrollment, the baseline levels of azotemia and and respiratory systems are very important for using
ammonia were low. However, in spite of the performed these methods in intensive therapy for children after
blood purification procedures, there were significant cardiac surgery. By the end of MARS-therapy, MAP
positive changes of urea and creatinine levels, which exceeded 25% of the baseline, but the need for
indicates that the efficiency of MARS and Prometheus inotropic support decreased. [32,33]
methods in eliminating water-soluble substances was
sufficiently high to allow their use in AKI and ALF in the Due to the large heat loss during extracorporeal
setting of MODS. [39,44]
According to many authors, the impact of
extracorporeal blood purification methods on survival
rate in ALF was statistically insignificant. However,
the results of multi-center prospective randomized
studies for this issue were ambiguous.
In the HELIOS study including 145 patients with
acute-on-chronic liver dysfunction receiving 8-10
Prometheus procedures, the increase in total survival
rate was statistically insignificant. However, the
subgroup of patients with the most severe condition, Figure 3: Dynamics of the fractions of bilirubin during molecular
i.e. with hepatorenal syndrome type I and MELD score adsorbent recirculating system-therapy (4-month patient)
54 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 27, 2017