Page 207 - Read Online
P. 207
Bilovol et al. Relationship between atrial fibrillation, BMI and adipokines
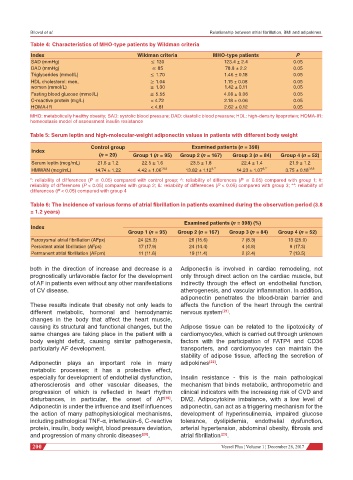
Table 4: Characteristics of MHO-type patients by Wildman criteria
Index Wildman criteria MHO-type patients P
SAD (mmHg) ≤ 130 123.4 ± 2.4 0.05
DAD (mmHg) ≤ 85 78.8 ± 2.2 0.05
Triglycerides (mmol/L) ≤ 1.70 1.46 ± 0.18 0.05
HDL cholesterol: men, ≥ 1.04 1.15 ± 0.08 0.05
women (mmol/L) ≥ 1.30 1.42 ± 0.11 0.05
Fasting blood glucose (mmol/L) ≤ 5.55 4.08 ± 0.06 0.05
C-reactive protein (mg/L) < 4.72 2.18 ± 0.06 0.05
HOMA-IR < 4.81 2.62 ± 0.12 0.05
MHO: metabolically healthy obesity; SAD: systolic blood pressure; DAD: diastolic blood pressure; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; HOMA-IR:
homeostasis model of assessment insulin resistance
Table 5: Serum leptin and high-molecular-weight adiponectin values in patients with different body weight
Control group Examined patients (n = 398)
Index
(n = 20) Group 1 (n = 95) Group 2 (n = 167) Group 3 (n = 84) Group 4 (n = 52)
Serum leptin (mcg/mL) 21.6 ± 1.2 22.5 ± 1.6 23.5 ± 1.8 22.4 ± 1.4 21.9 ± 1.2
HMWAN (mcg/mL) 14.74 ± 1.22 4.42 ± 1.06 *,#,& 13.82 ± 1.12 &,** 14.23 ± 1.07 &,** 3.75 ± 0.18 *,#,&
*: reliability of differences (P ≤ 0.05) compared with control group; ^: reliability of differences (P ≤ 0.05) compared with group 1; #:
reliability of differences (P < 0.05) compared with group 2; &: reliability of differences (P < 0.05) compared with group 3; **: reliability of
differences (P < 0.05) compared with group 4
Table 6: The incidence of various forms of atrial fibrillation in patients examined during the observation period (3.8
± 1.2 years)
Examined patients (n = 398) (%)
Index
Group 1 (n = 95) Group 2 (n = 167) Group 3 (n = 84) Group 4 (n = 52)
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (AFpx) 24 (25.3) 26 (15.6) 7 (8.3) 13 (25.0)
Persistent atrial fibrillation (AFps) 17 (17.9) 24 (14.4) 4 (4.8) 9 (17.3)
Permanent atrial fibrillation (AFpm) 11 (11.6) 19 (11.4) 2 (2.4) 7 (13.5)
both in the direction of increase and decrease is a Adiponectin is involved in cardiac remodeling, not
prognostically unfavorable factor for the development only through direct action on the cardiac muscle, but
of AF in patients even without any other manifestations indirectly through the effect on endothelial function,
of CV disease. atherogenesis, and vascular inflammation. In addition,
adiponectin penetrates the blood-brain barrier and
These results indicate that obesity not only leads to affects the function of the heart through the central
different metabolic, hormonal and hemodynamic nervous system [21] .
changes in the body that affect the heart muscle,
causing its structural and functional changes, but the Adipose tissue can be related to the lipotoxicity of
same changes are taking place in the patient with a cardiomyocytes, which is carried out through unknown
body weight deficit, causing similar pathogenesis, factors with the participation of FATP4 and CD36
particularly AF development. transporters, and cardiomyocytes can maintain the
stability of adipose tissue, affecting the secretion of
Adiponectin plays an important role in many adipokines [22] .
metabolic processes; it has a protective effect,
especially for development of endothelial dysfunction, Insulin resistance - this is the main pathological
atherosclerosis and other vascular diseases, the mechanism that binds metabolic, anthropometric and
progression of which is reflected in heart rhythm clinical indicators with the increasing risk of CVD and
disturbances, in particular, the onset of AF [19] . DM2. Adipocytokine imbalance, with a low level of
Adiponectin is under the influence and itself influences adiponectin, can act as a triggering mechanism for the
the action of many pathophysiological mechanisms, development of hyperinsulinemia, impaired glucose
including pathological TNF-α, interleukin-6, C-reactive tolerance, dyslipidemia, endothelial dysfunction,
protein, insulin, body weight, blood pressure deviation, arterial hypertension, abdominal obesity, fibrosis and
and progression of many chronic diseases [20] . atrial fibrillation [23] .
200 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017