Page 206 - Read Online
P. 206
Bilovol et al. Relationship between atrial fibrillation, BMI and adipokines
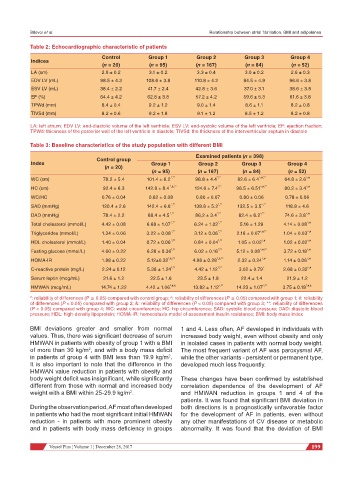
Table 2: Echocardiographic characteristic of patients
Control Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4
Indices
(n = 20) (n = 95) (n = 167) (n = 84) (n = 52)
LA (sm) 2.9 ± 0.2 3.1 ± 0.2 3.3 ± 0.4 3.0 ± 0.2 2.6 ± 0.3
EDV LV (mL) 98.5 ± 4.3 108.6 ± 3.8 110.8 ± 4.2 84.5 ± 4.9 96.6 ± 3.8
ESV LV (mL) 38.4 ± 2.2 41.7 ± 2.4 42.8 ± 3.6 37.0 ± 3.1 38.6 ± 3.8
EF (%) 64.4 ± 4.2 62.8 ± 3.8 57.2 ± 4.2 59.6 ± 5.3 61.6 ± 3.8
TPWd (mm) 8.4 ± 0.4 9.2 ± 1.2 9.0 ± 1.4 8.6 ± 1.1 8.2 ± 0.8
TIVSd (mm) 8.2 ± 0.6 9.2 ± 1.8 9.1 ± 1.2 8.5 ± 1.2 8.2 ± 0.8
LA: left atrium; EDV LV: end-diastolic volume of the left ventricle; ESV LV: end-systolic volume of the left ventricle; EF: ejection fraction;
TPWd: thickness of the posterior wall of the left ventricle in diastole; TIVSd: the thickness of the interventricular septum in diastole
Table 3: Baseline characteristics of the study population with different BMI
Examined patients (n = 398)
Control group
Index Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4
(n = 20)
(n = 95) (n = 167) (n = 84) (n = 52)
WC (sm) 78.2 ± 5.4 101.4 ± 6.2 *,** 96.8 ± 4.4 *,** 82.6 ± 6.4 ^,#,** 64.8 ± 2.6 ^,#
HC (sm) 92.4 ± 6.3 142.8 ± 8.4 *,&,** 124.6 ± 7.4 *,** 96.5 ± 6.51 ^,#,** 80.2 ± 3.4 ^,#
WC/HC 0.76 ± 0.04 0.82 ± 0.08 0.80 ± 0.07 0.80 ± 0.06 0.78 ± 0.06
SAD (mmHg) 120.4 ± 2.6 142.4 ± 6.8 *,** 138.8 ± 5.2 *,** 132.5 ± 3.5 ^,** 118.8 ± 4.6
DAD (mmHg) 78.4 ± 2.2 88.4 ± 4.5 *,** 86,2 ± 3.4 *,** 82.4 ± 6.2 ^,** 74.6 ± 3.8 ^,#
Total cholesterol (mmol/L) 4.42 ± 0.08 6.68 ± 1.07 *,** 6.24 ± 1.02 *,** 5.16 ± 1.29 4.14 ± 0.08 ^,#
Triglycerides (mmol/L) 1.34 ± 0.06 3.22 ± 0.08 *,** 3.12 ± 0.06 *,** 2.16 ± 0.07 ^,#,** 1.04 ± 0.03 ^,#
HDL cholesterol (mmol/L) 1.40 ± 0.04 0.72 ± 0.06 *,** 0.84 ± 0.04 *,** 1.05 ± 0.02 ^,# 1.02 ± 0.02 ^,#
Fasting glucose (mmol/L) 4.60 ± 0.22 6.28 ± 0.36 *,** 6.02 ± 0.16 *,** 5.12 ± 0.08 ^,#,** 3.72 ± 0.18 ^,#
HOMA-IR 1.88 ± 0.22 5.12±0.32 *,&,** 4.98 ± 0.28 *,&,** 2.32 ± 0.24 ^,# 1.14 ± 0.06 ^,#
C-reactive protein (mg/L) 2.24 ± 0.12 5.38 ± 1.24 *,** 4.42 ± 1.12 *,** 3.02 ± 0.79 ^ 2.68 ± 0.32 ^,#
Serum leptin (mcg/mL) 21.6 ± 1.2 22.5 ± 1.6 23.5 ± 1.8 22.4 ± 1.4 21.9 ± 1.2
HMWAN (mcg/mL) 14.74 ± 1.22 4.42 ± 1.06 *,#,& 13.82 ± 1.12 ^,** 14.23 ± 1.07 ^,** 3.75 ± 0.18 *,#,&
*: reliability of differences (P ≤ 0.05) compared with control group; ^: reliability of differences (P ≤ 0.05) compared with group 1; #: reliability
of differences (P < 0.05) compared with group 2; &: reliability of differences (P < 0.05) compared with group 3; **: reliability of differences
(P < 0.05) compared with group 4; WC: waist circumference; HC: hip circumference; SAD: systolic blood pressure; DAD: diastolic blood
pressure; HDL: high-density lipoprotein; HOMA-IR: homeostasis model of assessment insulin resistance; BMI: body mass index
BMI deviations greater and smaller from normal 1 and 4. Less often, AF developed in individuals with
values. Thus, there was significant decrease of serum increased body weight, even without obesity and only
HMWAN in patients with obesity of group 1 with a BMI in isolated cases in patients with normal body weight.
of more than 30 kg/m , and with a body mass deficit The most frequent variant of AF was paroxysmal AF,
2
in patients of group 4 with BMI less than 19.9 kg/m . while the other variants - persistent or permanent type,
2
It is also important to note that the difference in the developed much less frequently.
HMWAN value reduction in patients with obesity and
body weight deficit was insignificant, while significantly These changes have been confirmed by established
different from those with normal and increased body correlation dependence of the development of AF
weight with a BMI within 25-29.9 kg/m . and HMWAN reduction in groups 1 and 4 of the
2
patients. It was found that significant BMI deviation in
During the observation period, AF most often developed both directions is a prognostically unfavorable factor
in patients who had the most significant initial HMWAN for the development of AF in patients, even without
reduction - in patients with more prominent obesity any other manifestations of CV disease or metabolic
and in patients with body mass deficiency in groups abnormality. It was found that the deviation of BMI
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017 199