Page 211 - Read Online
P. 211
Wang et al. Adipokines in metabolism, and cardiovascular system
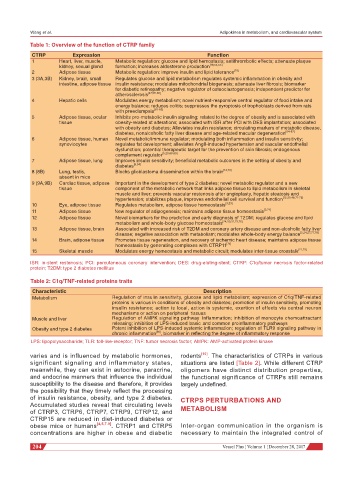
Table 1: Overview of the function of CTRP family
CTRP Expression Function
1 Heart, liver, muscle, Metabolic regulation: glucose and lipid hemostasis; antithrombotic effects; attenuate plaque
kidney, sexual gland formation; increases aldosterone production [18,54,55]
2 Adipose tissue Metabolic regulation: improve insulin and lipid tolerance [18]
3 (3A,3B) Kidney, brain, small Regulates glucose and lipid metabolism regulates systemic inflammation in obesity and
intestine, adipose tissue insulin resistance; modulates mitochondrial biogenesis; attenuate liver fibrosis; biomarker
for diabetic retinopathy; negative regulator of osteoclastogenesis; independent predictor for
atherosclerosis [47,56-60]
4 Hepatic cells Modulates energy metabolism; novel nutrient-responsive central regulator of food intake and
energy balance; reduces colitis; suppresses the pyroptosis of trophoblasts derived from rats
with preeclampsia [61-63]
5 Adipose tissue, ocular Inhibits pro-metabolic insulin signaling; related to the degree of obesity and is associated with
tissue obesity-related at alterations; associated with ISR after PCI with DES implantation; associated
with obesity and diabetes; Alleviates insulin resistance; circulating markers of metabolic disease,
diabetes, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and age-related macular degeneration [64-67]
6 Adipose tissue, human Novel metabolic/immune regulator; modulating both inflammation and insulin sensitivity;
synoviocytes regulates fat development; alleviates AngII-induced hypertension and vascular endothelial
dysfunction; potential therapeutic target for the prevention of skin fibrosis; endogenous
complement regulator [5,29,68,69]
7 Adipose tissue, lung Improves insulin sensitivity; beneficial metabolic outcomes in the setting of obesity and
diabetes [9,54]
8 (8B) Lung, testis, Blocks glioblastoma dissemination within the brain [14,70]
absent in mice
9 (9A,9B) Cardiac tissue, adipose Important in the development of type 2 diabetes; novel metabolic regulator and a new
tissue component of the metabolic network that links adipose tissue to lipid metabolism in skeletal
muscle and liver; prevents vascular restenosis after angioplasty, hepatic steatosis and
hypertension; stabilizes plaque, improves endothelial cell survival and function [12,20,48,71-73]
10 Eye, adipose tissue Regulates metabolism, adipose tissue homeostasis [3,23]
11 Adipose tissue New regulator of adipogenesis; maintains adipose tissue homeostasis [3,74]
12 Adipose tissue Novel biomarkers for the prediction and early diagnosis of T2DM; regulates glucose and lipid
metabolism and whole-body glucose homeostasis [24,50,51,75,76]
13 Adipose tissue, brain Associated with increased risk of T2DM and coronary artery disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease; negative association with metabolism; modulates whole-body energy balance [2,24,27,77,78]
14 Brain, adipose tissue Promotes tissue regeneration, and recovery of ischemic heart disease; maintains adipose tissue
homeostasis by generating complexes with CTRP11 [74]
15 Skeletal muscle Modulates energy homeostasis and metabolic circuit; modulates inter-tissue crosstalk [21,79]
ISR: in-stent restenosis; PCI: percutaneous coronary intervention; DES: drug-eluting-stent; CTRP: C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related
protein; T2DM: type 2 diabetes mellitus
Table 2: C1q/TNF-related proteins traits
Characteristic Description
Metabolism Regulation of insulin sensitivity, glucose and lipid metabolism; expression of C1q/TNF-related
proteins is various in conditions of obesity and diabetes; promotion of insulin sensitivity, promoting
insulin resistance; action is local, action is systemic, exertion of effects via central neuron
mechanisms or action on peripheral tissues
Muscle and liver Regulation of AMPK signaling pathway Inflammation; inhibition of monocyte chemoattractant
releasing; inhibition of LPS-induced basic and common proinflammatory pathways
Obesity and type 2 diabetes Potent inhibition of LPS-induced systemic inflammation; regulation of TLR9 signaling pathway in
chronic inflammation [80] , biomarker in reflecting the degree of inflammatory response
LPS: lipopolysaccharide; TLR: toll-like-receptor; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase
varies and is influenced by metabolic hormones, rodents [10] . The characteristics of CTRPs in various
significant signaling and inflammatory states, situations are listed [Table 2]. While different CTRP
meanwhile, they can exist in autocrine, paracrine, oligomers have distinct distribution properties,
and endocrine manners that influence the individual the functional significance of CTRPs still remains
susceptibility to the disease and therefore, it provides largely undefined.
the possibility that they timely reflect the processing
of insulin resistance, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. CTRPS PERTURBATIONS AND
Accumulated studies reveal that circulating levels METABOLISM
of CTRP3, CTRP6, CTRP7, CTRP9, CTRP12, and
CTRP15 are reduced in diet-induced diabetes or
obese mice or humans [4,5,7-9] . CTRP1 and CTRP5 Inter-organ communication in the organism is
concentrations are higher in obese and diabetic necessary to maintain the integrated control of
204 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ December 28, 2017