Page 153 - Read Online
P. 153
Page 22 of 43 Rao. Vessel Plus 2022;6:26 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.93
Figure 39. An apical four-chamber view showing the truncus (Tr) overriding the ventricular septum and ventricular septal defect (VSD)
(arrow). Reproduced from Ref. [28] . LV: Left ventricle; RV: right ventricle.
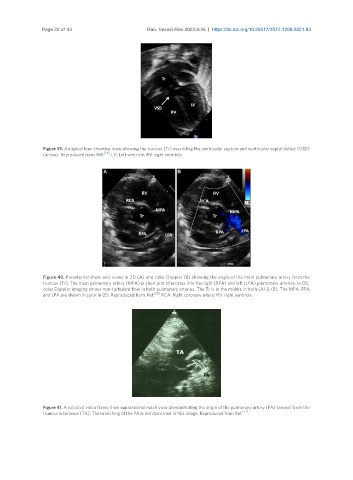
Figure 40. Parasternal short-axis views in 2D (A) and color Doppler (B) showing the origin of the main pulmonary artery from the
truncus (Tr). The main pulmonary artery (MPA) is short and bifurcates into the right (RPA) and left (LPA) pulmonary arteries. In (B),
color Doppler imaging shows non-turbulent flow in both pulmonary arteries. The Tr is in the middle in both (A) & (B). The MPA, RPA
and LPA are shown in color in (B). Reproduced from Ref. [28] . RCA: Right coronary artery; RV: right ventricle.
Figure 41. A selected video frame from suprasternal notch view demonstrating the origin of the pulmonary artery (PA) (arrow) from the
[22]
truncus arteriosus (TA). The branching of the PA is not discerned in this image. Reproduced from Ref. .