Page 12 - Read Online
P. 12
Romano et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:31 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.24 Page 9 of 15
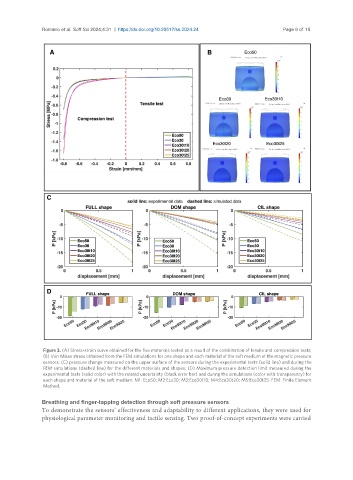
Figure 3. (A) Stress-strain curve obtained for the five materials tested as a result of the combination of tensile and compression tests;
(B) Von Mises stress obtained from the FEM simulations for one shape and each material of the soft medium of the magnetic pressure
sensors; (C) pressure change measured on the upper surface of the sensors during the experimental tests (solid line) and during the
FEM simulations (dashed line) for the different materials and shapes; (D) Maximum pressure detection limit measured during the
experimental tests (solid color) with the related uncertainty (black error bar) and during the simulations (color with transparency) for
each shape and material of the soft medium. M1: Eco50; M2:Eco30; M3:Eco30t10; M4:Eco30t20; M5:Eco30t25. FEM: Finite Element
Method.
Breathing and finger-tapping detection through soft pressure sensors
To demonstrate the sensors’ effectiveness and adaptability to different applications, they were used for
physiological parameter monitoring and tactile sensing. Two proof-of-concept experiments were carried