Page 196 - Read Online
P. 196
Page 26 of 39 Jeon et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 1 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.35
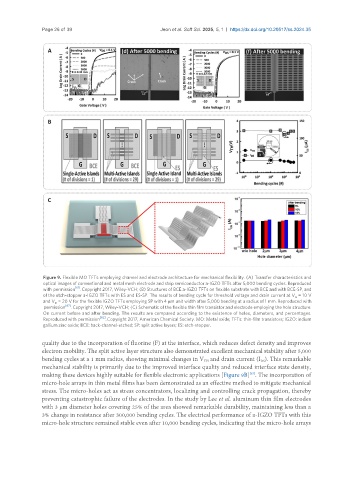
Figure 9. Flexible MO TFTs employing channel and electrode architecture for mechanical flexibility. (A) Transfer characteristics and
optical images of conventional and metal mesh electrode and strip semiconductor a-IGZO TFTs after 5,000 bending cycles. Reproduced
with permission [61] . Copyright 2017, Wiley-VCH; (B) Structures of BCE a-IGZO TFTs on flexible substrate with BCE and with BCE-SP, and
of the etch-stopper a-IGZO TFTs with ES and ES-SP. The results of bending cycle for threshold voltage and drain current at V = 10 V
G
and V = 20 V for the flexible IGZO TFTs employing SP with 4 μm unit width after 5,000 bending at a radius of 1 mm. Reproduced with
D
permission [67] . Copyright 2017, Wiley-VCH; (C) Schematic of the flexible thin film transistor and electrode employing the hole structure.
On current before and after bending. The results are compared according to the existence of holes, diameters, and percentages.
Reproduced with permission [62] . Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. MO: Metal oxide; TFTs: thin-film transistors; IGZO: indium
gallium zinc oxide; BCE: back-channel-etched; SP: split active layers; ES: etch-stopper.
quality due to the incorporation of fluorine (F) at the interface, which reduces defect density and improves
electron mobility. The split active layer structure also demonstrated excellent mechanical stability after 5,000
bending cycles at a 1 mm radius, showing minimal changes in V and drain current (I ). This remarkable
TH
DS
mechanical stability is primarily due to the improved interface quality and reduced interface state density,
making these devices highly suitable for flexible electronic applications [Figure 9B] . The incorporation of
[67]
micro-hole arrays in thin metal films has been demonstrated as an effective method to mitigate mechanical
stress. The micro-holes act as stress concentrators, localizing and controlling crack propagation, thereby
preventing catastrophic failure of the electrodes. In the study by Lee et al. aluminum thin film electrodes
with 3 μm diameter holes covering 25% of the area showed remarkable durability, maintaining less than a
3% change in resistance after 300,000 bending cycles. The electrical performance of a-IGZO TFTs with this
micro-hole structure remained stable even after 10,000 bending cycles, indicating that the micro-hole arrays