Page 193 - Read Online
P. 193
Jeon et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 1 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.35 Page 23 of 39
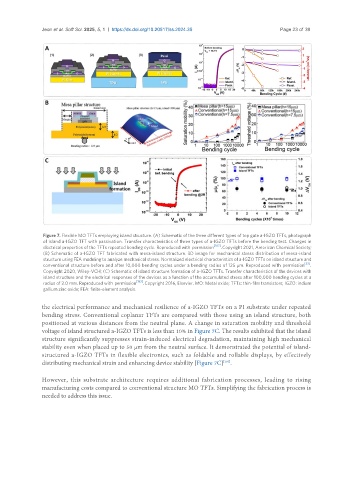
Figure 7. Flexible MO TFTs employing island structure. (A) Schematic of the three different types of top gate a-IGZO TFTs, photograph
of island a-IGZO TFT with passivation. Transfer characteristics of three types of a-IGZO TFTs before the bending test. Changes in
electrical properties of the TFTs repeated bending cycle. Reproduced with permission [102] . Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society;
(B) Schematic of a-IGZO TFT fabricated with mesa-island structure. 3D image for mechanical stress distribution of mesa-island
structure using FEA modeling to analyze mechanical stress. Normalized electrical characteristics of a-IGZO TFTs on island structure and
conventional structure before and after 10,000 bending cycles under a bending radius of 125 μm. Reproduced with permission [33] .
Copyright 2020, Wiley-VCH; (C) Schematic of island structure formation of a-IGZO TFTs. Transfer characteristics of the devices with
island structure and the electrical responses of the devices as a function of the accumulated stress after 100,000 bending cycles at a
[193]
radius of 2.0 mm. Reproduced with permission . Copyright 2016, Elsevier. MO: Metal oxide; TFTs: thin-film transistors; IGZO: indium
gallium zinc oxide; FEA: finite-element analysis.
the electrical performance and mechanical resilience of a-IGZO TFTs on a PI substrate under repeated
bending stress. Conventional coplanar TFTs are compared with those using an island structure, both
positioned at various distances from the neutral plane. A change in saturation mobility and threshold
voltage of island structured a-IGZO TFTs is less than 10% in Figure 7C. The results exhibited that the island
structure significantly suppresses strain-induced electrical degradation, maintaining high mechanical
stability even when placed up to 50 µm from the neutral surface. It demonstrated the potential of island-
structured a-IGZO TFTs in flexible electronics, such as foldable and rollable displays, by effectively
distributing mechanical strain and enhancing device stability [Figure 7C] .
[193]
However, this substrate architecture requires additional fabrication processes, leading to rising
manufacturing costs compared to conventional structure MO TFTs. Simplifying the fabrication process is
needed to address this issue.