Page 61 - Read Online
P. 61
Villeda-Hernandez et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:14 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.52 Page 17 of 35
Table 6. Combustion gas evolution [103]
Combustion reactions
Combustion of methane
CH (g) + 2O (g) → CO (g) + 2H O
4 2 2 2
Combustion of ethane
2C H (g) + 7O (g) → 4CO (g) + 6H O
2
6
2
2
2
Combustion of butane
2C H (g) +13O (g) → 8CO (g) + 10H O
2
2
4
2
10
Combustion of propane
C H (g) + 5O (g) → 3CO (g) + 4H O
2
2
3
2
8
Table 7. Thermal decomposition reactions for gas evolution [108]
Thermal decomposition reactions
Decomposition of sodium bicarbonate
2NaHCO (s) → Na CO (s) + H O (g) + CO (g)
3 2 3 2 2
Decomposition of sodium azide
2NaN (s) → 2Na (s) + 3N (g)
3 2
Decomposition of mercury oxide
2HgO (s) → 2Hg (l) + O (g)
2
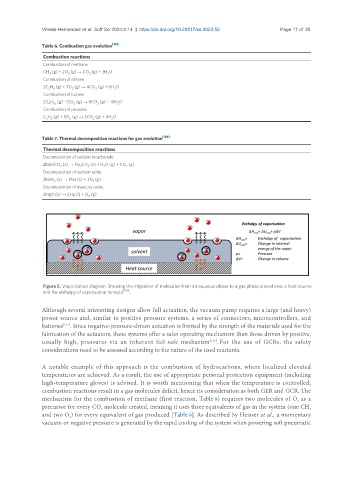
Figure 5. Vaporization diagram. Showing the migration of molecules from an aqueous phase to a gas phase placed over a heat source
[110]
and the enthalpy of vaporization formula .
Although several interesting designs allow full actuation, the vacuum pump requires a large (and heavy)
power source and, similar to positive pressure systems, a series of connectors, microcontrollers, and
[115]
batteries . Since negative-pressure-driven actuation is limited by the strength of the materials used for the
fabrication of the actuators, these systems offer a safer operating mechanism than those driven by positive,
[116]
usually high, pressures via an inherent fail-safe mechanism . For the use of GCRs, the safety
considerations need to be assessed according to the nature of the used reactants.
A notable example of this approach is the combustion of hydrocarbons, where localized elevated
temperatures are achieved. As a result, the use of appropriate personal protection equipment (including
high-temperature gloves) is advised. It is worth mentioning that when the temperature is controlled,
combustion reactions result in a gas molecules deficit, hence its consideration as both GER and GCR. The
mechanism for the combustion of methane (first reaction, Table 8) requires two molecules of O as a
2
precursor for every CO molecule created, meaning it uses three equivalents of gas in the system (one CH
4
2
and two O ) for every equivalent of gas produced [Table 8]. As described by Heisser et al., a momentary
2
vacuum or negative pressure is generated by the rapid cooling of the system when powering soft pneumatic