Page 59 - Read Online
P. 59
Bai et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:40 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.38 Page 25 of 34
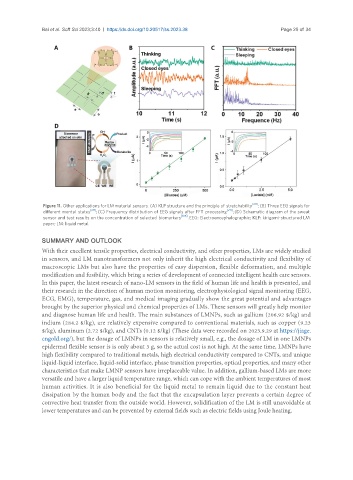
Figure 11. Other applications for LM material sensors. (A) KLP structure and the principle of stretchability [211] ; (B) Three EEG signals for
different mental states [211] ; (C) Frequency distribution of EEG signals after FFT processing [211] ; (D) Schematic diagram of the sweat
sensor and test results on the concentration of selected biomarkers [186] . EEG: Electroencephalographic; KLP: kirigami-structured LM
paper; LM: liquid metal.
SUMMARY AND OUTLOOK
With their excellent tensile properties, electrical conductivity, and other properties, LMs are widely studied
in sensors, and LM nanotransformers not only inherit the high electrical conductivity and flexibility of
macroscopic LMs but also have the properties of easy dispersion, flexible deformation, and multiple
modification and fusibility, which bring a series of development of connected intelligent health care sensors.
In this paper, the latest research of nano-LM sensors in the field of human life and health is presented, and
their research in the direction of human motion monitoring, electrophysiological signal monitoring (EEG,
ECG, EMG), temperature, gas, and medical imaging gradually show the great potential and advantages
brought by the superior physical and chemical properties of LMs. These sensors will greatly help monitor
and diagnose human life and health. The main substances of LMNPs, such as gallium (206.92 $/kg) and
indium (284.2 $/kg), are relatively expensive compared to conventional materials, such as copper (9.23
$/kg), aluminum (2.72 $/kg), and CNTs (0.12 $/kg) (These data were recorded on 2023.9.29 at https://jiage.
cngold.org/), but the dosage of LMNPs in sensors is relatively small, e.g., the dosage of LM in one LMNPs
epidermal flexible sensor is is only about 3 g, so the actual cost is not high. At the same time, LMNPs have
high flexibility compared to traditional metals, high electrical conductivity compared to CNTs, and unique
liquid-liquid interface, liquid-solid interface, phase transition properties, optical properties, and many other
characteristics that make LMNP sensors have irreplaceable value. In addition, gallium-based LMs are more
versatile and have a larger liquid temperature range, which can cope with the ambient temperatures of most
human activities. It is also beneficial for the liquid metal to remain liquid due to the constant heat
dissipation by the human body and the fact that the encapsulation layer prevents a certain degree of
convective heat transfer from the outside world. However, solidification of the LM is still unavoidable at
lower temperatures and can be prevented by external fields such as electric fields using Joule heating.