Page 56 - Read Online
P. 56
Page 22 of 34 Bai et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:40 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.38
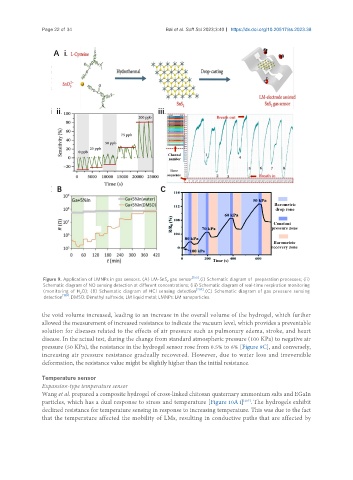
Figure 9. Application of LMNPs in gas sensors. (A) LM-SnS gas sensor [155] . (i) Schematic diagram of preparation processes; (ii)
2
Schematic diagram of NO sensing detection at different concentrations; (iii) Schematic diagram of real-time respiration monitoring
(monitoring of H O); (B) Schematic diagram of HCl sensing detection [204] . (C) Schematic diagram of gas pressure sensing
2
detection [189] . DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide; LM liquid metal; LMNPs: LM nanoparticles.
the void volume increased, leading to an increase in the overall volume of the hydrogel, which further
allowed the measurement of increased resistance to indicate the vacuum level, which provides a preventable
solution for diseases related to the effects of air pressure such as pulmonary edema, stroke, and heart
disease. In the actual test, during the change from standard atmospheric pressure (100 KPa) to negative air
pressure (50 KPa), the resistance in the hydrogel sensor rose from 0.5% to 6% [Figure 9C], and conversely,
increasing air pressure resistance gradually recovered. However, due to water loss and irreversible
deformation, the resistance value might be slightly higher than the initial resistance.
Temperature sensor
Expansion-type temperature sensor
Wang et al. prepared a composite hydrogel of cross-linked chitosan quaternary ammonium salts and EGaIn
[207]
particles, which has a dual response to stress and temperature [Figure 10A i] . The hydrogels exhibit
declined resistance for temperature sensing in response to increasing temperature. This was due to the fact
that the temperature affected the mobility of LMs, resulting in conductive paths that are affected by