Page 142 - Read Online
P. 142
Tian et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:30 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.21 Page 17 of 27
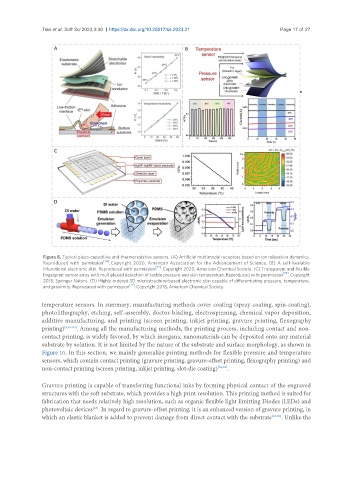
Figure 8. Typical piezo-capacitive and thermoresistive sensors. (A) Artificial multimodal receptors based on ion relaxation dynamics.
Reproduced with permission [24] . Copyright 2020, American Association for the Advancement of Science. (B) A self-healable
bifunctional electronic skin. Reproduced with permission [72] . Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society. (C) Transparent and flexible
fingerprint sensor array with multiplexed detection of tactile pressure and skin temperature. Reproduced with permission [73] . Copyright
2018, Springer Nature. (D) Highly ordered 3D microstructure-based electronic skin capable of differentiating pressure, temperature,
[77]
and proximity. Reproduced with permission . Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society.
temperature sensors. In summary, manufacturing methods cover coating (spray-coating, spin-coating),
photolithography, etching, self-assembly, doctor-blading, electrospinning, chemical vapor deposition,
additive manufacturing, and printing (screen printing, inkjet printing, gravure printing, flexography
printing) [3,81-83] . Among all the manufacturing methods, the printing process, including contact and non-
contact printing, is widely favored, by which inorganic nanomaterials can be deposited onto any material
substrate by solution. It is not limited by the nature of the substrate and surface morphology, as shown in
Figure 10. In this section, we mainly generalize printing methods for flexible pressure and temperature
sensors, which contain contact printing (gravure printing, gravure-offset printing, flexography printing) and
non-contact printing (screen printing, inkjet printing, slot-die coating) [82,83] .
Gravure printing is capable of transferring functional inks by forming physical contact of the engraved
structures with the soft substrate, which provides a high print resolution. This printing method is suited for
fabrication that needs relatively high resolution, such as organic flexible light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) and
photovoltaic devices . In regard to gravure-offset printing, it is an enhanced version of gravure printing, in
[84]
which an elastic blanket is added to prevent damage from direct contact with the substrate [83,89] . Unlike the