Page 320 - Read Online
P. 320
Page 6 of 14 Darbinyan et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2018;5:41 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.33
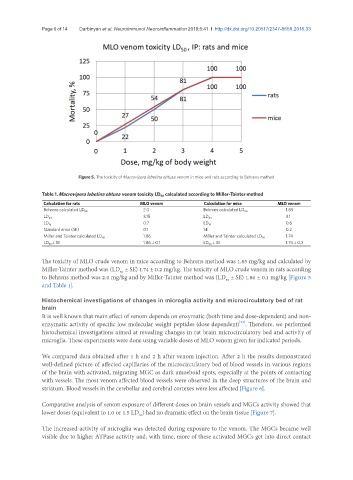
Figure 5. The toxicity of Macrovipera lebetina obtusa venom in mice and rats according to Behrens method
Table 1. Macrovipera lebetina obtusa venom toxicity LD 50 calculated according to Miller-Tainter method
Calculation for rats MLO venom Calculation for mice MLO venom
2.0 1.85
Behrens calculated LD 50 Behrens calculated LD 50
3.15 3.1
LD 84 LD 84
0.7 0.6
LD 16 LD 16
Standard error (SE) 0.1 SE 0.2
1.86 1.74
Miller and Tainter calculated LD 50 Miller and Tainter calculated LD 50
LD 50 ± SE 1.86 ± 0.1 LD 50 ± SE 1.74 ± 0.2
The toxicity of MLO crude venom in mice according to Behrens method was 1.85 mg/kg and calculated by
Miller-Tainter method was (LD ± SE) 1.74 ± 0.2 mg/kg. The toxicity of MLO crude venom in rats according
50
to Behrens method was 2.0 mg/kg and by Miller-Tainter method was (LD ± SE) 1.86 ± 0.1 mg/kg [Figure 5
50
and Table 1].
Histochemical investigations of changes in microglia activity and microcirculatory bed of rat
brain
It is well known that main effect of venom depends on enzymatic (both time and dose-dependent) and non-
[24]
enzymatic activity of specific low molecular weight peptides (dose dependent) . Therefore, we performed
histochemical investigations aimed at revealing changes in rat brain microcirculatory bed and activity of
microglia. These experiments were done using variable doses of MLO venom given for indicated periods.
We compared data obtained after 1 h and 2 h after venom injection. After 2 h the results demonstrated
well-defined picture of affected capillaries of the microcirculatory bed of blood vessels in various regions
of the brain with activated, migrating MGC as dark amoeboid spots, especially at the points of contacting
with vessels. The most venom affected blood vessels were observed in the deep structures of the brain and
striatum. Blood vessels in the cerebellar and cerebral cortexes were less affected [Figure 6].
Comparative analysis of venom exposure of different doses on brain vessels and MGCs activity showed that
lower doses (equivalent to 1.0 or 1.5 LD ) had no dramatic effect on the brain tissue [Figure 7].
50
The increased activity of microglia was detected during exposure to the venom. The MGCs became well
visible due to higher ATPase activity and, with time, more of these activated MGCs get into direct contact