Page 319 - Read Online
P. 319
Darbinyan et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2018;5:41 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.33 Page 5 of 14
Figure 3. A sample of microglial cell contouring for footprint and linear dimensions measurement. The left slice - contoured cell of the brain, 1 h
after injection, the right slice - 2 h after injection
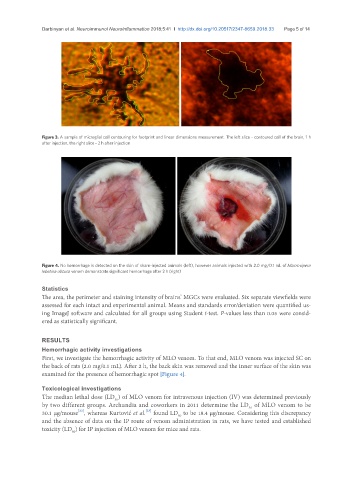
Figure 4. No hemorrhage is detected on the skin of sham-injected animals (left), however animals injected with 2.0 mg/0.1 mL of Macrovipera
lebetina obtusa venom demonstrate significant hemorrhage after 2 h (right)
Statistics
The area, the perimeter and staining intensity of brains’ MGCs were evaluated. Six separate viewfields were
assessed for each intact and experimental animal. Means and standards error/deviation were quantified us-
ing ImageJ software and calculated for all groups using Student t-test. P-values less than 0.05 were consid-
ered as statistically significant.
RESULTS
Hemorrhagic activity investigations
First, we investigate the hemorrhagic activity of MLO venom. To that end, MLO venom was injected SC on
the back of rats (2.0 mg/0.1 mL). After 2 h, the back skin was removed and the inner surface of the skin was
examined for the presence of hemorrhagic spot [Figure 4].
Toxicological investigations
The median lethal dose (LD ) of MLO venom for intravenous injection (IV) was determined previously
50
by two different groups. Archundia and coworkers in 2011 determine the LD of MLO venom to be
50
[22]
30.1 µg/mouse , whereas Kurtović et al. found LD to be 18.4 µg/mouse. Considering this discrepancy
[23]
50
and the absence of data on the IP route of venom administration in rats, we have tested and established
toxicity (LD ) for IP injection of MLO venom for mice and rats.
50