Page 48 - Read Online
P. 48
the embryonic yolk sac that are then seeded in the in neuronal circuit development and maintaining
rudimentary brain and persist there into adulthood. [1] tissue homeostasis indicates that they have a basal
Another school of scientists thought that their entry in physiological function from developing embryo to
brain from blood also occurs at some points in embryonic growing adult. [11,13] In the present study our attempt is to
and early natal phases, which also gradually populates find that basal morphological and behavioural variation
into entire brain and designated as microglia. [2-5] of microglia from embryo to growing brain up to its
Microglia function like a hybrids of glia and leukocytes maturation, excluding aging brain. With identifying in
and thus express a variety of cytokine receptors as well situ distribution and morphological transformation, we
as producing cytokines themselves. Microglia forms also isolated them to assess the morphological differences
[6]
an extremely stable population in brain and comprise and functional deviation in terms of phagocytosis.
up to 20% of total glial population forming an immune
accessory network. [7,8] Microglia can adapt according to METHODS
the central nervous system (CNS) microenvironment,
monitor the CNS integrity and also act under the strict Animal and grouping
control of neurobiochemical environment. Recent The Sprague-Dawley rats were maintained for the
studies indicate that they function in maintaining experiment as approved by institutional animal
normal tissue homeostasis in brain at the resting state ethical committee (Approval No. -AG/CP/IAEC-
through scanning their territorial domains. [9-11] They WBSU/2011-12/5) and according to the animal
phagocytose cellular debris, contribute to restructuring experiment procedures strictly followed the “Principles
neuronal circuits and triggering repair, which are of Laboratory Animal Care” (NIH publication no. 85-
assumed to be related with development. [12-16] Depending 23, revised in 1985). The animals were fed with pellet
on specific environmental context microglia play a dual diet, or equivalent, and water ad libitum, 12 h light and
role of neuroprotection or neurotoxic. [12,17-19] dark cycle were maintained, examined and weighed at
regular interval throughout the experimental period.
There are few studies which showed that microglial Reproductively matured male and receptive female were
morphology changes with age, but most of the studies set for breeding at a rate of 1:2 respectively, examined
have dealt with their changes in neuropathological for confirmation of mating usually made by visualising
conditions. Microglial transformation from ramified the copulatory plug, after that pregnant mothers were
[20]
to amoeboid affects their functional modifications. The separated and pregnancy days were counted to obtain
[22]
effector role of the cells are mostly studied in disease the required embryos. Neonates were maintained
[21]
models or subjects, But seldom has any attempt been with their respective mothers in one cage as they were
made to evaluate the baseline physiological response at waning age. The groups of animals maintained were
of the cells in a normally developing brain beginning (1) early embryo (ED 10 ± 1); (2) late embryo (ED 18 ± 2);
at birth. However, recent findings showing their role (3) neonate (D 5 ± 1); (4) young adult (D45 ± 5) and (5)
mature adult (D 240 ± 10).
Histological sectioning of brain tissue and haematoxylin-
eosin staining
The rats were deeply anaesthetized with sodium
pentobarbital (50 mg/kg body weight). The whole brain
was dissected out, initially placed in ice cold Phosphate
Buffer Saline (PBS) and then postfixed in 10% buffered
formalin (NICE, India) for overnight at 4 °C. After fixation,
foetal, postnatal and adult brains were washed in PBS,
dehydrated through graded alcohol (30%, 50%, 70%,
95% and absolute alcohol) and embedded in paraffin
(MERCK, India) through histokinate processing. From
this block coronal sections of brain were cut at 5-7 µm
thickness with a microtome (WESWOXTM OPTIK
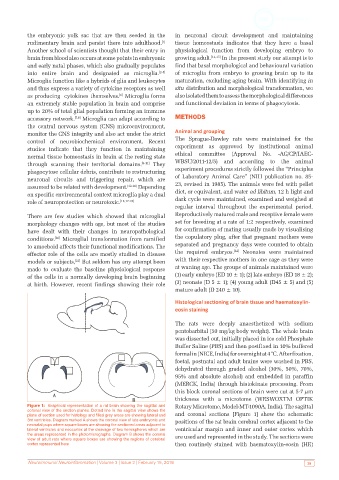
Figure 1: Graphical representation of a rat brain showing the sagittal and Rotary Microtome, Model-MT-1090A, India). The sagittal
coronal view of the section planes. Dotted line in the sagittal view shows the
plane of section used for histology and filled grey areas are showing lateral and and coronal sections [Figure 1] show the schematic
3rd ventricles. Diagram marked A shows the coronal view of late embryonic and positions of the rat brain cerebral cortex adjacent to the
neonatal pups where square boxes are showing the sectioned areas adjacent to
lateral ventricles and neocortex at the cleavage of two hemispheres which are ventricular margin and inner and outer cortex which
the areas represented in the photomicrographs. Diagram B shows the coronal are used and represented in the study. The sections were
view of adult rats where square boxes are showing the regions of cerebral
cortex represented here then routinely stained with haematoxylin-eosin (HE)
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 3 | Issue 2 | February 15, 2016 39