Page 104 - Read Online
P. 104
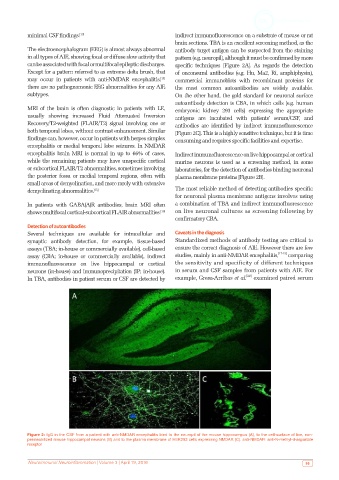
minimal CSF findings. [13] indirect immunofluorescence on a substrate of mouse or rat
brain sections. TBA is an excellent screening method, as the
The electroencephalogram (EEG) is almost always abnormal antibody target antigen can be suspected from the staining
in all types of AIE, showing focal or diffuse slow activity that pattern (e.g. neuropil), although it must be confirmed by more
can be associated with focal or multifocal epileptic discharges. specific techniques [Figure 2A]. As regards the detection
Except for a pattern referred to as extreme delta brush, that of onconeural antibodies (e.g. Hu, Ma2, Ri, amphiphysin),
[14]
may occur in patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis, commercial immunoblots with recombinant proteins for
there are no pathognomonic EEG abnormalities for any AIE the most common autoantibodies are widely available.
subtypes. On the other hand, the gold standard for neuronal surface
autoantibody detection is CBA, in which cells (e.g. human
MRI of the brain is often diagnostic in patients with LE, embryonic kidney 293 cells) expressing the appropriate
usually showing increased Fluid Attenuated Inversion antigens are incubated with patients’ serum/CSF, and
Recovery/T2-weighted (FLAIR/T2) signal involving one or antibodies are identified by indirect immunofluorescence
both temporal lobes, without contrast enhancement. Similar [Figure 2C]. This is a highly sensitive technique, but it is time
findings can, however, occur in patients with herpes simplex consuming and requires specific facilities and expertise.
encephalitis or medial temporal lobe seizures. In NMDAR
encephalitis brain MRI is normal in up to 66% of cases, Indirect immunofluorescence on live hippocampal or cortical
while the remaining patients may have unspecific cortical murine neurons is used as a screening method, in some
or subcortical FLAIR/T2 abnormalities, sometimes involving laboratories, for the detection of antibodies binding neuronal
the posterior fossa or medial temporal regions, often with plasma membrane proteins [Figure 2B].
small areas of demyelination, and more rarely with extensive
demyelinating abnormalities. [15] The most reliable method of detecting antibodies specific
for neuronal plasma membrane antigens involves using
In patients with GABA(A)R antibodies, brain MRI often a combination of TBA and indirect immunofluorescence
shows multifocal cortical-subcortical FLAIR abnormalities. [16] on live neuronal cultures as screening following by
confirmatory CBA.
Detection of autoantibodies
Several techniques are available for intracellular and Caveats in the diagnosis
synaptic antibody detection, for example, tissue-based Standardized methods of antibody testing are critical to
assays (TBA; in-house or commercially available), cell-based ensure the correct diagnosis of AIE. However there are few
assay (CBA; in-house or commercially available), indirect studies, mainly in anti-NMDAR encephalitis, [17-19] comparing
immunofluorescence on live hippocampal or cortical the sensitivity and specificity of different techniques
neurons (in-house) and immunoprecipitation (IP; in-house). in serum and CSF samples from patients with AIE. For
[20]
In TBA, antibodies in patient serum or CSF are detected by example, Gresa-Arribas et al. examined paired serum
Figure 2: IgG in the CSF from a patient with anti-NMDAR encephalitis bind to the neuropil of the mouse hippocampus (A), to the cell-surface of live, non-
permeabilized mouse hippocampal neurons (B) and to the plasma membrane of HEK293 cells expressing NMDAR (C). anti-NMDAR: anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate
receptor
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 3 | April 19, 2016 95