Page 108 - Read Online
P. 108
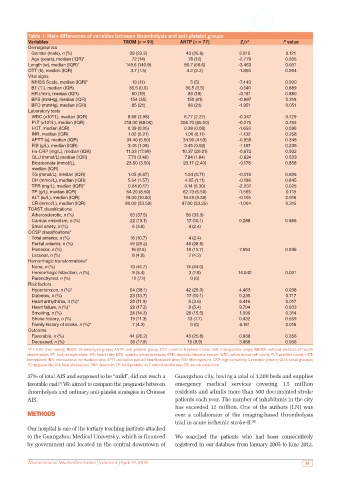
Table 1: Main differences of variables between thrombolysis and anti-platelet groups
Variables TROM (n = 91) ANTP (n = 77) Z/x 2 P value
Demographics
Gender (male), n (%) 39 (23.2) 43 (25.6) 2.815 0.121
Age (years), median (IQR)* 72 (14) 76 (12) -2.779 0.005
Length (w), median (IQR)* 149.6 (140.9) 90.7 (69.6) -3.463 0.001
OTT (h), median (IQR) 3.7 (1.5) 4.2 (2.2) -1.855 0.064
Vital signs
NIHSS Scale, median (IQR)* 13 (11) 5 (5) -7.443 0.000
BT (℃), median (IQR) 36.5 (0.6) 36.5 (0.5) -0.140 0.889
HR (/min), median (IQR) 80 (19) 80 (18) -0.151 0.880
BPS (mmHg), median (IQR) 154 (35) 150 (41) -0.997 0.319
BPD (mmHg), median (IQR) 85 (21) 80 (21) -1.951 0.051
Laboratory tests
WBC (×10 /L), median (IQR) 8.66 (3.98) 8.77 (2.27) -0.347 0.729
9
PLT (×10 /L), median (IQR) 218.00 (68.00) 206.70 (65.00) -0.275 0.783
9
HCT, median (IQR) 0.39 (0.05) 0.38 (0.08) -1.653 0.098
INR, median (IQR) 1.02 (0.21) 1.06 (0.11) -1.132 0.258
APTT (s), median (IQR) 34.40 (5.60) 34.90 (4.53) -0.939 0.348
FIB (g/L), median (IQR) 3.45 (1.09) 3.45 (0.92) -1.187 0.235
Hs-CRP (mg/L), median (IQR) 11.33 (17.99) 10.37 (20.01) -0.672 0.502
GLU (mmol/L),median (IQR) 7.70 (3.40) 7.84 (1.84) -0.624 0.533
Bicarbonate (mmol/L), 23.50 (3.50) 23.17 (2.40) -0.178 0.858
median (IQR)
TG (mmol/L), median (IQR) 1.05 (0.67) 1.04 (0.71) -0.516 0.606
CH (mmol/L), median (IQR) 5.04 (1.57) 4.95 (1.11) -0.196 0.845
TPR (mg/L), median (IQR)* 0.04 (0.17) 0.14 (0.30) -2.237 0.025
TP (g/L), median (IQR) 64.20 (8.50) 62.73 (5.50) -1.565 0.118
ALT (iu/L), median (IQR) 19.00 (10.00) 19.48 (9.39) -0.105 0.916
CR (mmol/L), median (IQR) 80.00 (33.50) 87.00 (33.35) -1.004 0.315
TOAST classifications
Atherosclerotic, n (%) 63 (37.5) 56 (33.3)
Cardiac embolism, n (%) 22 (13.1) 17 (10.1) 0.288 0.866
Small artery, n (%) 6 (3.6) 4 (2.4)
OCSP classifications*
Total anterior, n (%) 18 (10.7) 4 (2.4)
Partial anterior, n (%) 49 (29.2) 48 (28.6)
Posterior, n (%) 16 (9.5) 18 (10.7) 7.993 0.046
Lacunar, n (%) 8 (4.8) 7 (4.2)
Hemorrhagic transformations*
None, n (%) 70 (41.7) 74 (44.0)
Hemorrhagic Infarction, n (%) 9 (5.4) 3 (1.8) 14.042 0.001
Parenchymal, n (%) 12 (7.1) 0 (0)
Risk factors
Hypertension, n (%)* 64 (38.1) 42 (25.0) 4.463 0.038
Diabetes, n (%) 23 (13.7) 17 (10.1) 0.235 0.717
Heart arrhythmia, n (%)* 20 (11.9) 6 (3.6) 6.416 0.017
Heart failure, n (%)* 29 (17.3) 9 (5.4) 9.704 0.003
Smoking, n (%) 24 (14.3) 26 (15.5) 1.090 0.314
Stroke history, n (%) 19 (11.3) 13 (7.7) 0.432 0.559
Family history of stroke, n (%)* 7 (4.2) 0 (0) 6.181 0.016
Outcome
Favorable, n (%) 44 (26.2) 43 (25.6) 0.938 0.356
Deceased, n (%) 30 (17.9) 15 (8.9) 3.868 0.056
*P < 0.05 (two tailed); TROM: thrombolysis group; ANTP: anti-platelet group; OTT: onset to treatment time; IQR: interquartile range; NIHSS: national institute of health
stroke scale; BT: body temperature; HR: heart rate; BPS: systolic blood pressure; BPD: diastolic blood pressure; WBC: white blood cell count; PLT: platelet count; HCT:
hematocrit; INR: international normalized ratio; APTT: activated partial thromboplastin time; FIB: fibrinogen; hs-CRP: high sensitivity C reactive protein; GLU: blood glucose;
TG: triglyceride; CH: total cholesterol; TRP: troponin; TP: total protein; ALT: aminotransferase; CR: serum creatinine
37% of total AIS and supposed to be “mild”, did not reach a Guangzhou city, having a total of 1,200 beds and supplies
favorable end. We aimed to compare the prognosis between emergency medical services covering 1.5 million
[3]
thrombolysis and ordinary anti-platelet strategies in Chinese residents and admits more than 500 documented stroke
AIS. patients each year. The number of inhabitants in the city
has exceeded 12 million. One of the authors (LN) was
METHODS ever a collaborator of the imaging-based thrombolysis
trial in acute ischemic stroke-II. [4]
Our hospital is one of the tertiary teaching institute attached
to the Guangzhou Medical University, which is financed We searched the patients who had been consecutively
by government and located in the central downtown of registered in our database from January 2005 to June 2012.
Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 3 | April 19, 2016 99