Page 163 - Read Online
P. 163
Table 2: Predisposing factors of brain abscess
Types of predisposing Number of Total predisposing Without predisposing Total
factors predisposing factors factors (%) factors (%)
Postsurgery 8 73 (45.06) 89 (54.94) 162
Penetrating injury 11
CSOM/mastoiditis 22
Congenital heart disease 10
Infective endocarditis 3
Frontal sinusitis 12
Ethmoidal sinusitis 4
Immunocompromised 3
CSOM: chronic suppurative otitis media
Table 3: Site distribution
Types of abscess Frontal Temporal Parietal Occipital Cerebellar Ganglio‑thalamic zone
Acute pyogenic (113) 34 25 16 18 13 7
Chronic pyogenic (29) 10 9 4 3 3 0
Tubercular (14) 3 3 2 1 4 1
Aspergillus (3) 2 ‑ ‑ 1 ‑ ‑
Abscess in metastesis (3) ‑ ‑ ‑ 1 1 1
Total (%) 49 (30.2) 37 (22.8) 22 (13.6) 24 (14.8) 21 (12.96) 9 (5.5)
Table 4: Types of operations, residual neuro‑deficit and outcome
Operations Number Mortality Residual major neuro‑deficit Complete
recovery
Single burr hole aspiration 111 (68.5%) 11 4 (hemiparesis, motor dysphasia, hand weakness, footdrop) 96
Multiple aspiration 34 (21%) 9 3 (monoparesis, sensory dysphasia, visual field defect) 22
Third ventriculoscopic (endoscopic) 1 (0.62%) 0 0 1
drainage and ETV [Figure 6]
Excision of abscess by craniotomy 16 (9.87%) 2 2 (nominal dysphasia, monoparesis) 12
Total 162 22 (13.58%) 9 (5.55%) 131 (80.86%)
ETV: endoscopic third ventriculostomy
b
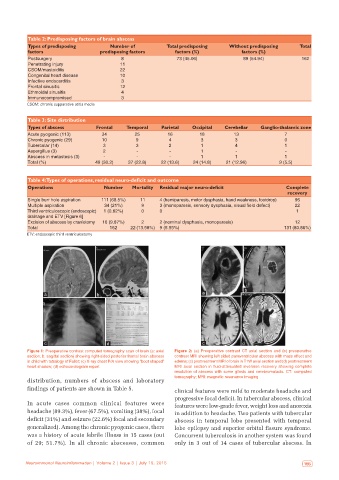
a b a
c d c d
Figure 1: Preoperative contrast computed tomography scan of brain (a: axial Figure 2: (a) Preoperative contrast CT axial section and (b) preoperative
section; b: sagittal section) showing right‑sided posterior frontal brain abscess contrast MRI showing left sided paraventricular abscess with mass effect and
in child with tetralogy of Fallot; (c) X‑ray chest P/A view showing “boot shaped” edema; (c) posttreatment MRI of brain in T1W axial section and (d) posttreatment
heart shadow; (d) echocardiogram report MRI axial section in fluid‑attenuated inversion recovery showing complete
resolution of abscess with some gliosis and cerebromalacia. CT: computed
tomography; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging
distribution, numbers of abscess and laboratory
findings of patients are shown in Table 5. clinical features were mild to moderate headache and
progressive focal deficit. In tubercular abscess, clinical
In acute cases common clinical features were features were low-grade fever, weight loss and anorexia
headache (89.3%), fever (67.5%), vomiting (38%), focal in addition to headache. Two patients with tubercular
deficit (31%) and seizure (22.6%) focal and secondary abscess in temporal lobe presented with temporal
generalized). Among the chronic pyogenic cases, there lobe epilepsy and superior orbital fissure syndrome.
was a history of acute febrile illness in 15 cases (out Concurrent tuberculosis in another system was found
of 29; 51.7%). In all chronic abscesses, common only in 3 out of 14 cases of tubercular abscess. In
154 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 3 | July 15, 2015 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 3 | July 15, 2015 155