Page 166 - Read Online
P. 166
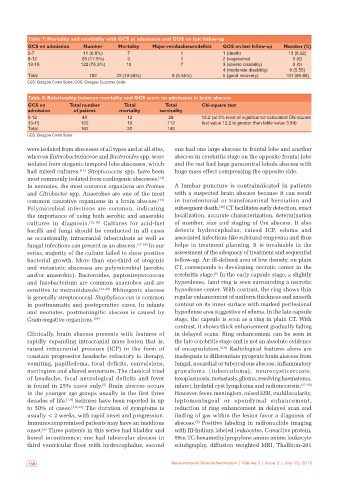
Table 7: Mortality and morbidity with GCS at admission and GOS on last follow‑up
GCS on admission Number Mortality Major residualneurodeficit GOS on last follow‑up Number (%)
3‑7 11 (6.8%) 7 1 1 (death) 13 (8.02)
8‑12 29 (17.9%) 5 1 2 (vegetative) 0 (0)
13‑15 122 (75.3%) 10 7 3 (severe disability) 0 (0)
4 (moderate disability) 9 (5.55)
Total 162 22 (13.58%) 9 (5.55%) 5 (good recovery) 131 (80.86)
GCS: Glasgow Coma Scale; GOS: Glasgow Outcome Scale
Table 8: Relationship between mortality and GCS score on admission in brain abscess
GCS on Total number Total Total Chi‑square test
admission of patient mortality survivality
3‑12 40 12 28 12.2 (at 5% level of significance calculated Chi‑square
13‑15 122 10 112 test value 12.2 is greater than table value 3.84)
Total 162 22 140
GCS: Glasgow Coma Scale
were isolated from abscesses of all types and at all sites, one had one large abscess in frontal lobe and another
whereas Enterobacteriaceae and Bacteroides spp. were abscess in cerebritis stage on the opposite frontal lobe
isolated from otogenic temporal lobe abscesses, which and the rest had large paracentral lobule abscess with
had mixed cultures. [13] Streptococcus spp. have been huge mass effect compressing the opposite side.
most commonly isolated from cardiogenic abscesses. [14]
In neonates, the most common organisms are Proteus A lumbar puncture is contraindicated in patients
and Citrobacter spp. Anaerobes are one of the most with a suspected brain abscess because it can result
common causative organisms in a brain abscess. [15] in transtentorial or transforaminal herniation and
Polymicrobial infections are common, indicating subsequent death. CT facilitates early detection, exact
[26]
the importance of using both aerobic and anaerobic localization, accurate characterization, determination
cultures in diagnosis. [15,16] Cultures for acid-fast of number, size and staging of the abscess. It also
bacilli and fungi should be conducted in all cases detects hydrocephalus, raised ICP, edema and
as occasionally, intracranial tuberculosis as well as associated infections like subdural empyema and thus
fungal infections can present as an abscess. [17-20] In our helps in treatment planning. It is invaluable in the
series, majority of the culture failed to show positive assessment of the adequacy of treatment and sequential
bacterial growth. More than one-third of otogenic follow-up. An ill-defined area of low density, on plain
and metastatic abscesses are polymicrobial (aerobic CT, corresponds to developing necrotic center in the
[6]
and/or anaerobic). Bacteroides, peptostreptococcus cerebritis stage. In the early capsule stage, a slightly
and fusobacterium are common anaerobes and are hyperdense, faint ring is seen surrounding a necrotic
sensitive to metronidazole. [21-23] Rhinogenic abscess hypodense center. With contrast, the ring shows thin
is generally streptococcal. Staphylococcus is common regular enhancement of uniform thickness and smooth
in posttraumatic and postoperative cases. In infants contour on its inner surface with marked perilesional
and neonates, postmeningitic abscess is caused by hypodense area suggestive of edema. In the late capsule
Gram-negative organisms. [24] stage, the capsule is seen as a ring in plain CT. With
contrast, it shows thick enhancement gradually fading
Clinically, brain abscess presents with features of in delayed scans. Ring enhancement can be seen in
rapidly expanding intracranial mass lesion that is, the late cerebritis stage and is not an absolute evidence
raised intracranial pressure (ICP) in the form of of encapsulation. [8,9] Radiological features alone are
constant progressive headache refractory to therapy, inadequate to differentiate pyogenic brain abscess from
vomiting, papilledema, focal deficits, convulsions, fungal, nocardial or tuberculous abscess, inflammatory
meningism and altered sensorium. The classical triad granuloma (tuberculoma), neurocysticercosis,
of headache, focal neurological deficits and fever toxoplasmosis, metastasis, glioma, resolving haematoma,
is found in 25% cases only. Brain abscess occurs infarct, hydatid cyst lymphoma and radionecrosis. [27-30]
[5]
in the younger age groups usually in the first three However, fever, meningism, raised ESR, multilocularity,
decades of life. [1,6] Seizures have been reported in up leptomeningeal or ependymal enhancement,
to 50% of cases. [1,6,25] The duration of symptoms is reduction of ring enhancement in delayed scan and
usually < 2 weeks, with rapid onset and progression. finding of gas within the lesion favor a diagnosis of
Immunocompromised patients may have an insidious abscess. Positive labeling in radionuclide imaging
[9]
onset. Three patients in this series had bladder and with III-Indium labeled leukocytes, C-reactive protein,
[6]
bowel incontinence; one had tubercular abscess in 99m TC-hexamethylpropylene amine oxime leukocyte
third ventricular floor with hydrocephalus, second scintigraphy, diffusion weighted MRI, Thallium-201
158 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 3 | July 15, 2015 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 3 | July 15, 2015 159