Page 164 - Read Online
P. 164
a b
a b
c d
c d
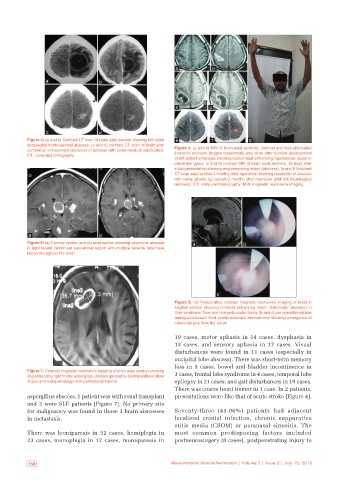
Figure 3: (a and b) Contrast CT scan of brain axial section showing left sided e f g
parasagital fronto‑parietal abscess; (c and d) contrast CT scan of brain after
completion of treatment resolution of abscess with some residual calcification. Figure 4: (a and b) MRI of brain axial sections, contrast and fluid‑attenuated
CT: computed tomography inversion recovery images respectively was done after sudden development
of left sided hemiplegia showing noncontrast enhancing hypointense lesion in
precentral gyrus; (c and d) contrast MRI of brain axial sections, 16 days after
initial presentation showing ring enhancing lesion (abscess); (e and f) (contrast
CT scan axial section 3 months after operation) showing resolution of abscess
with some gliosis; (g) patient‑3 months after operation (with full neurological
recovery). CT: computed tomography; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging
a b
Figure 5: (a) Coronal section and (b) axial section showing tubercular abscess a b
in right lateral ventricular subcallosal region with multiple satellite tubercular
lesion throughout the brain
c
Figure 6: (a) Preoperative contrast magnetic resonance imaging of brain in
sagittal section showing contrast enhancing lesion (tubercular abscess) in
third ventricular floor and interpeduncular fossa; (b and c) per operative picture
during endoscopic third ventriculoscopic interventions showing emergence of
tubercular pus from the lesion
19 cases, motor aphasia in 14 cases, dysphasia in
13 cases, and sensory aphasia in 17 cases. Visual
disturbances were found in 11 cases (especially in
occipital lobe abscess). There was short-term memory
loss in 5 cases, bowel and bladder incontinence in
Figure 7: Contrast magnetic resonance imaging of brain axial section showing 3 cases, frontal lobe syndrome in 4 cases, temporal lobe
ring enhancing right frontal aspergillus abscess (proved by postoperative culture
of pus and histopathology) with perilesional edema epilepsy in 21 cases, and gait disturbances in 19 cases.
There was coarse hemi tremor in 1 case. In 2 patients,
aspergillus abscess, 1 patient was with renal transplant presentations were like that of acute stroke [Figure 4].
and 2 were SLE patients [Figure 7]. No primary site
for malignancy was found in those 3 brain abscesses Seventy-three (45.06%) patients had adjacent
in metastasis. localized cranial infection, chronic suppurative
otitis media (CSOM) or paranasal sinusitis. The
There was hemiparesis in 52 cases, hemiplegia in most common predisposing factors included
23 cases, monoplegia in 12 cases, monoparesis in postneurosurgery (8 cases), postpenetrating injury to
156 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 3 | July 15, 2015 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 2 | Issue 3 | July 15, 2015 157