Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
Page 10 of 21 Ponsero et al. Microbiome Res Rep 2023;2:27 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/mrr.2023.26
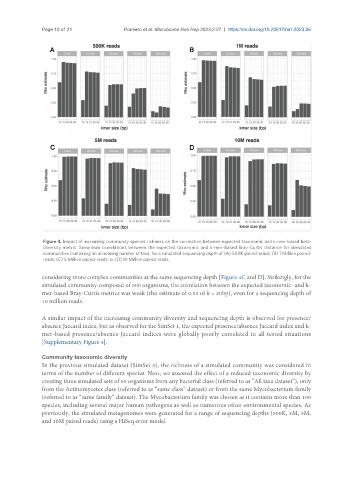
Figure 4. Impact of increasing community species richness on the correlation between expected taxonomic and k-mer-based beta-
diversity metric. Spearman correlations between the expected taxonomic and k-mer-based Bray-Curtis distance for simulated
communities containing an increasing number of taxa, for a simulated sequencing depth of (A) 500K paired-reads; (B) 1 Million paired-
reads; (C) 5 Million paired-reads; or (D) 10 Million paired-reads.
considering more complex communities at the same sequencing depth [Figure 4C and D]. Strikingly, for the
simulated community composed of 500 organisms, the correlation between the expected taxonomic- and k-
mer-based Bray-Curtis metrics was weak (rho estimate of 0.52 of k = 20bp), even for a sequencing depth of
10 million reads.
A similar impact of the increasing community diversity and sequencing depth is observed for presence/
absence Jaccard index, but as observed for the SimSet 1, the expected presence/absence Jaccard index and k-
mer-based presence/absence Jaccard indices were globally poorly correlated in all tested situations
[Supplementary Figure 4].
Community taxonomic diversity
In the previous simulated dataset (SimSet 3), the richness of a simulated community was considered in
terms of the number of different species. Next, we assessed the effect of a reduced taxonomic diversity by
creating three simulated sets of 50 organisms from any bacterial class (referred to as “All taxa dataset”), only
from the Actinomycetes class (referred to as “same class” dataset) or from the same Mycobacterium family
(referred to as “same family” dataset). The Mycobacterium family was chosen as it contains more than 100
species, including several major human pathogens as well as numerous other environmental species. As
previously, the simulated metagenomes were generated for a range of sequencing depths (500K, 1M, 5M,
and 10M paired reads) using a HiSeq error model.