Page 62 - Read Online
P. 62
Page 14 of 21 Ponsero et al. Microbiome Res Rep 2023;2:27 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/mrr.2023.26
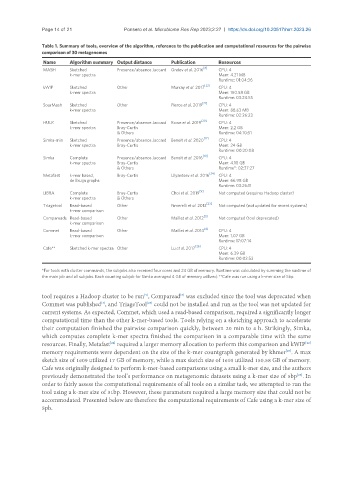
Table 1. Summary of tools, overview of the algorithm, reference to the publication and computational resources for the pairwise
comparison of 30 metagenomes
Name Algorithm summary Output distance Publication Resources
[8]
MASH Sketched Presence/absence Jaccard Ondov et al. 2016 CPU: 4
k-mer spectra Mem: 4.21 MB
Runtime: 01:04:36
kWIP Sketched Other Murray et al. 2017 [22] CPU: 4
k-mer spectra Mem: 150.58 GB
Runtime: 03:24:55
[21]
SourMash Sketched Other Pierce et al. 2019 CPU: 4
k-mer spectra Mem: 88.63 MB
Runtime: 02:26:23
HULK Sketched Presence/absence Jaccard Rowe et al. 2019 [20] CPU: 4
k-mer spectra Bray-Curtis Mem: 2.2 GB
& Others Runtime: 04:10:51
[17]
Simka-min Sketched Presence/absence Jaccard Benoit et al. 2020 CPU: 4
k-mer spectra Bray-Curtis Mem: 24 GB
Runtime: 00:20:08
[10]
Simka Complete Presence/absence Jaccard Benoit et al. 2016 CPU: 4
k-mer spectra Bray-Curtis Mem: 4.10 GB
& Others Runtime*: 02:37:27
Metafast k-mer based, Bray-Curtis Ulyantsev et al. 2016 [24] CPU: 4
de Bruijn graphs Mem: 66.98 GB
Runtime: 03:26:11
[9]
LIBRA Complete Bray-Curtis Choi et al. 2019 Not computed (requires Hadoop cluster)
k-mer spectra & Others
[23]
Triagetool Read-based Other Fimerelli et al. 2013 Not computed (not updated for recent systems)
k-mer comparison
[3]
Compareads Read-based Other Maillet et al. 2012 Not computed (tool deprecated)
k-mer comparison
Commet Read-based Other Maillet et al. 2014 [4] CPU: 4
k-mer comparison Mem: 1.07 GB
Runtime: 17:07:14
[26]
Cafe** Sketched k-mer spectra Other Lu et al. 2017 CPU: 4
Mem: 6.39 GB
Runtime: 00:03:53
*For tools with cluster commands, the subjobs also received four cores and 24 GB of memory. Runtime was calculated by summing the runtime of
the main job and all subjobs. Each counting subjob for Simka averaged 4 GB of memory utilized; **Cafe was run using a k-mer size of 5bp.
tool requires a Hadoop cluster to be run , Comparead was excluded since the tool was deprecated when
[3]
[9]
Commet was published , and TriageTool could not be installed and run as the tool was not updated for
[4]
[23]
current systems. As expected, Commet, which used a read-based comparison, required a significantly longer
computational time than the other k-mer-based tools. Tools relying on a sketching approach to accelerate
their computation finished the pairwise comparison quickly, between 20 min to 4 h. Strikingly, Simka,
which computes complete k-mer spectra finished the comparison in a comparable time with the same
[22]
resources. Finally, Metafast required a larger memory allocation to perform this comparison and kWIP
[24]
memory requirements were dependent on the size of the k-mer countgraph generated by khmer . A max
[25]
sketch size of 1e09 utilized 17 GB of memory, while a max sketch size of 1e10 utilized 150.58 GB of memory.
Cafe was originally designed to perform k-mer-based comparisons using a small k-mer size, and the authors
previously demonstrated the tool’s performance on metagenomic datasets using a k-mer size of 5bp . In
[26]
order to fairly assess the computational requirements of all tools on a similar task, we attempted to run the
tool using a k-mer size of 31bp. However, these parameters required a large memory size that could not be
accommodated. Presented below are therefore the computational requirements of Cafe using a k-mer size of
5pb.