Page 57 - Read Online
P. 57
Ponsero et al. Microbiome Res Rep 2023;2:27 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/mrr.2023.26 Page 9 of 21
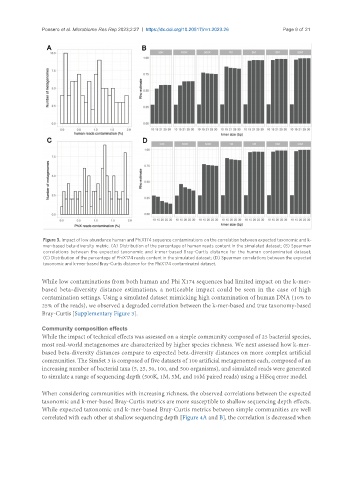
Figure 3. Impact of low abundance human and PhiX174 sequence contaminations on the correlation between expected taxonomic and k-
mer-based beta-diversity metric. (A) Distribution of the percentage of human reads content in the simulated dataset; (B) Spearman
correlations between the expected taxonomic and k-mer-based Bray-Curtis distance for the human contaminated dataset;
(C) Distribution of the percentage of PhiX174 reads content in the simulated dataset; (D) Spearman correlations between the expected
taxonomic and k-mer-based Bray-Curtis distance for the PhiX174 contaminated dataset.
While low contaminations from both human and Phi X174 sequences had limited impact on the k-mer-
based beta-diversity distance estimations, a noticeable impact could be seen in the case of high
contamination settings. Using a simulated dataset mimicking high contamination of human DNA (10% to
25% of the reads), we observed a degraded correlation between the k-mer-based and true taxonomy-based
Bray-Curtis [Supplementary Figure 3].
Community composition effects
While the impact of technical effects was assessed on a simple community composed of 25 bacterial species,
most real-world metagenomes are characterized by higher species richness. We next assessed how k-mer-
based beta-diversity distances compare to expected beta-diversity distances on more complex artificial
communities. The SimSet 3 is composed of five datasets of 100 artificial metagenomes each, composed of an
increasing number of bacterial taxa (5, 25, 50, 100, and 500 organisms), and simulated reads were generated
to simulate a range of sequencing depth (500K, 1M, 5M, and 10M paired reads) using a HiSeq error model.
When considering communities with increasing richness, the observed correlations between the expected
taxonomic and k-mer-based Bray-Curtis metrics are more susceptible to shallow sequencing depth effects.
While expected taxonomic and k-mer-based Bray-Curtis metrics between simple communities are well
correlated with each other at shallow sequencing depth [Figure 4A and B], the correlation is decreased when