Page 488 - Read Online
P. 488
Page 10 of 15 Smer et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:52 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.36
A B
C D
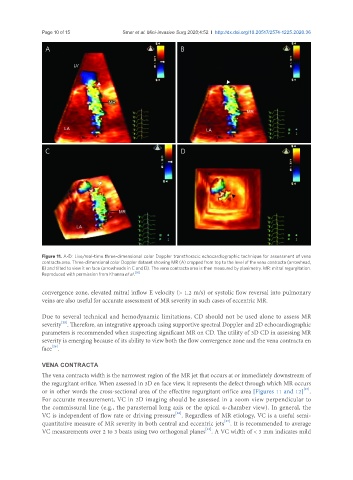
Figure 11. A-D: Live/real-time three-dimensional color Doppler transthoracic echocardiographic technique for assessment of vena
contracta area. Three-dimensional color Doppler dataset showing MR (A) cropped from top to the level of the vena contracta (arrowhead,
B) and tilted to view it en face (arrowheads in C and D). The vena contracta area is then measured by planimetry. MR: mitral regurgitation.
Reproduced with permission from Khanna et al. [30]
convergence zone, elevated mitral inflow E velocity (> 1.2 m/s) or systolic flow reversal into pulmonary
veins are also useful for accurate assessment of MR severity in such cases of eccentric MR.
Due to several technical and hemodynamic limitations, CD should not be used alone to assess MR
[22]
severity . Therefore, an integrative approach using supportive spectral Doppler and 2D echocardiographic
parameters is recommended when suspecting significant MR on CD. The utility of 3D CD in assessing MR
severity is emerging because of its ability to view both the flow convergence zone and the vena contracta en
face .
[26]
VENA CONTRACTA
The vena contracta width is the narrowest region of the MR jet that occurs at or immediately downstream of
the regurgitant orifice. When assessed in 3D en face view, it represents the defect through which MR occurs
or in other words the cross-sectional area of the effective regurgitant orifice area [Figures 11 and 12] .
[27]
For accurate measurement, VC in 2D imaging should be assessed in a zoom view perpendicular to
the commissural line (e.g., the parasternal long axis or the apical 4-chamber view). In general, the
[28]
VC is independent of flow rate or driving pressure . Regardless of MR etiology, VC is a useful semi-
[27]
quantitative measure of MR severity in both central and eccentric jets . It is recommended to average
[22]
VC measurements over 2 to 3 beats using two orthogonal planes . A VC width of < 3 mm indicates mild