Page 52 - Read Online
P. 52
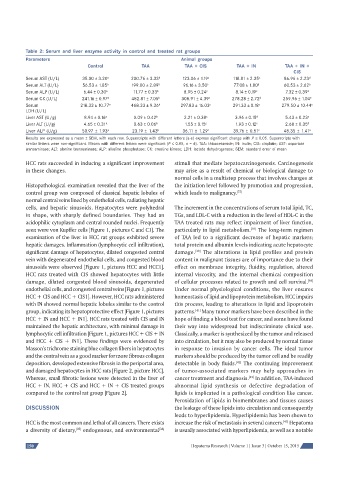
Table 2: Serum and liver enzyme activity in control and treated rat groups
Parameters Animal groups
Control TAA TAA + CIS TAA + IN TAA + IN +
CIS
Serum AST (U/L) 35.00 ± 3.20 a 200.76 ± 3.33 b 123.06 ± 1.19 c 118.81 ± 2.35 c 86.96 ± 2.23 d
Serum ALT (U/L) 56.53 ± 1.85 a 199.00 ± 2.89 b 96.16 ± 3.50 c 77.08 ± 1.80 d 60.53 ± 2.62 a
Serum ALP (U/L) 6.44 ± 0.30 a 11.77 ± 0.33 b 8.95 ± 0.24 c 8.14 ± 0.19 c 7.32 ± 0.39 d
Serum CK (U/L) 241.16 ± 0.97 a 482.81 ± 7.05 b 308.91 ± 4.39 c 278.28 ± 2.72 d 259.96 ± 1.04 e
Serum 218.33 ± 10.77 a 468.33 ± 9.36 b 297.83 ± 16.03 c 291.33 ± 0.18 c 279.50 ± 10.44 c
LDH (U/L)
Liver AST (U/g) 8.94 ± 0.16 a 0.09 ± 0.42 b 2.21 ± 0.38 c 3.96 ± 0.15 d 5.43 ± 0.23 e
Liver ALT (U/g) 4.65 ± 0.31 a 0.63 ± 0.06 b 1.55 ± 0.15 c 1.93 ± 0.12 c 2.68 ± 0.35 d
Liver ALP (U/g) 50.97 ± 1.93 a 23.19 ± 1.43 b 36.11 ± 1.29 c 39.76 ± 0.51 c 48.35 ± 1.41 a
Results are expressed as a mean ± SEM, with each row. Superscripts with different letters (a-e) express signifi cant change with P ≤ 0.05. Superscripts with
similar letters were non-signifi cant. Means with different letters were signifi cant (P ≤ 0.05, n = 6). TAA: thioacetamide; IN: inulin; CIS: cisplatin; AST: aspartate
transaminase; ALT: alanine transaminase; ALP: alkaline phosphatase; CK: creatine kinase; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; SEM: standard error of mean
HCC rats succeeded in inducing a significant improvement stimuli that mediate hepatocarcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis
in these changes. may arise as a result of chemical or biological damage to
normal cells in a multistep process that involves changes at
Histopathological examination revealed that the liver of the the initiation level followed by promotion and progression,
control group was composed of classical hepatic lobules of which leads to malignancy. [37]
normal central veins lined by endothelial cells, radiating hepatic
cells, and hepatic sinusoids. Hepatocytes were polyhedral The increment in the concentrations of serum total lipid, TC,
in shape, with sharply defined boundaries. They had an TGs, and LDL-C with a reduction in the level of HDL-C in the
acidophilic cytoplasm and central rounded nuclei. Frequently TAA treated rats may reflect impairment of liver function,
seen were von Kupffer cells [Figure 1, pictures C and C1]. The particularly in lipid metabolism. The long-term regimen
[38]
examination of the liver in HCC rat groups exhibited severe of TAA led to a significant decrease of hepatic markers;
hepatic damages. Inflammation (lymphocytic cell infiltration), total protein and albumin levels indicating acute hepatocyte
significant damage of hepatocytes, dilated congested central damage. The alterations in lipid profiles and protein
[39]
vein with degenerated endothelial cells, and congested blood content in malignant tissues are of importance due to their
sinusoids were observed [Figure 1, pictures HCC and HCC1]. effect on membrane integrity, fluidity, regulation, altered
HCC rats treated with CIS showed hepatocytes with little internal viscosity, and the internal chemical composition
damage, dilated congested blood sinusoids, degenerated of cellular processes related to growth and cell survival.
[40]
endothelial cells, and congested central veins [Figure 1, pictures Under normal physiological conditions, the liver ensures
HCC + CIS and HCC + CIS1]. However, HCC rats administered homeostasis of lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. HCC impairs
with IN showed normal hepatic lobules similar to the control this process, leading to alterations in lipid and lipoprotein
group, indicating its hepatoprotective effect [Figure 1, pictures patterns. Many tumor markers have been described in the
[41]
HCC + IN and HCC + IN1]. HCC rats treated with CIS and IN hope of finding a blood test for cancer, and some have found
maintained the hepatic architecture, with minimal damage in their way into widespread but indiscriminate clinical use.
lymphocytic cell infiltration [Figure 1, pictures HCC + CIS + IN Classically, a marker is synthesized by the tumor and released
and HCC + CIS + IN1]. These findings were evidenced by into circulation, but it may also be produced by normal tissue
Masson’s trichrome staining blue collagen fibers in hepatocytes in response to invasion by cancer cells. The ideal tumor
and the central vein as a good marker for more fibrous collagen markers should be produced by the tumor cell and be readily
deposition, developed extensive fibrosis in the periportal area, detectable in body fluids. The continuing improvement
[42]
and damaged hepatocytes in HCC rats [Figure 2, picture HCC]. of tumor-associated markers may help approaches in
Whereas, small fibrotic lesions were detected in the liver of cancer treatment and diagnosis. In addition, TAA-induced
[42]
HCC + IN, HCC + CIS and HCC + IN + CIS treated groups abnormal lipid synthesis or defective degradation of
compared to the control rat group [Figure 2]. lipids is implicated in a pathological condition like cancer.
Peroxidation of lipids in biomembranes and tissues causes
DISCUSSION the leakage of these lipids into circulation and consequently
leads to hyperlipidemia. Hyperlipidemia has been shown to
HCC is the most common and lethal of all cancers. There exists increase the risk of metastasis in several cancers. Hepatoma
[43]
a diversity of dietary, endogenous, and environmental is usually associated with hyperlipidemia, as well as a notable
[36]
[35]
150 Hepatoma Research | Volume 1 | Issue 3 | October 15, 2015