Page 63 - Read Online
P. 63
Page 24 of 30 Yoon et al. Energy Mater 2024;4:400063 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/energymater.2023.146
Table 5. Electrochemical performance of Sb-based ASSLIB anodes
Rate capability
Cyclability after the Xth cycle Current Reversible
Material Solid electrolyte ICE (%) -1 Ref.
(mAh g ) rate capacity
-1
-1
(A g ) (mAh g )
Sb/LLZO/C Li 6.25 Al 0.25 La Zr O 12 98.0 230 (X = 240) 0.5 240 [124]
3
2
GaSb/LiBH /C LiBH 97.2 400 (X = 400) 6.0 349 [125]
4 4
GaSb/LiBH /C LiBH 4 93.2 691 (X = 800) 3.3 380 [126]
4
Sb/LiBH /AB LiBH 95.0 621 (X = 50) - - [127]
4 4
Sb S /LiBH /AB LiBH 4 65.0 448 (X = 100) - - [128]
4
2 3
Sb Se /LiBH /AB LiBH 68.0 267 (X = 100) - - [128]
2 3 4 4
Sb Te /LiBH /AB LiBH 4 52.0 236 (X = 100) - - [128]
3
4
2
Sb S /LPS/AB LiBH 59.0 774 (X = 100) - - [129]
2 3 4
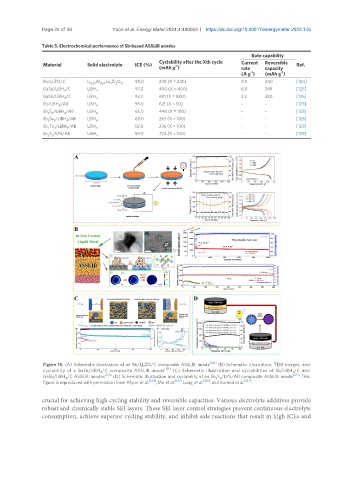
Figure 15. (A) Schematic illustration of an Sb/LLZO/C composite ASSLIB anode [124] . (B) Schematic illustration, TEM images, and
cyclability of a GaSb/LiBH /C composite ASSLIB anode [125] . (C) Schematic illustration and cyclabilities of Sb/LiBH /C and
4 4
[126] [127]
GaSb/LiBH /C ASSLIB anodes . (D) Schematic illustration and cyclability of an Sb S /LPS/AB composite ASSLIB anode . This
4 2 3
[124] [125] [126] [127]
figure is reproduced with permission from Afyon et al. , Mo et al. , Long et al. , and Kumari et al. .
crucial for achieving high cycling stability and reversible capacities. Various electrolyte additives provide
robust and chemically stable SEI layers. These SEI layer control strategies prevent continuous electrolyte
consumption, achieve superior cycling stability, and inhibit side reactions that result in high ICEs and