Page 177 - Read Online
P. 177
Rong et al. Vessel Plus 2019;3:18 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2019.007 Page 9 of 15
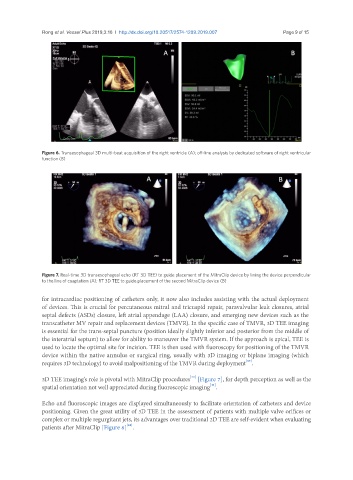
Figure 6. Transesophageal 3D multi-beat acquisition of the right ventricle (A); off-line analysis by dedicated software of right ventricular
function (B)
Figure 7. Real-time 3D transesophageal echo (RT 3D TEE) to guide placement of the MitraClip device by lining the device perpendicular
to the line of coaptation (A); RT 3D TEE to guide placement of the second MitraClip device (B)
for intracardiac positioning of catheters only, it now also includes assisting with the actual deployment
of devices. This is crucial for percutaneous mitral and tricuspid repair, paravalvular leak closures, atrial
septal defects (ASDs) closure, left atrial appendage (LAA) closure, and emerging new devices such as the
transcatheter MV repair and replacement devices (TMVR). In the specific case of TMVR, 3D TEE imaging
is essential for the trans-septal puncture (position ideally slightly inferior and posterior from the middle of
the interatrial septum) to allow for ability to maneuver the TMVR system. If the approach is apical, TEE is
used to locate the optimal site for incision. TEE is then used with fluoroscopy for positioning of the TMVR
device within the native annulus or surgical ring, usually with 3D imaging or biplane imaging (which
[39]
requires 3D technology) to avoid malpositioning of the TMVR during deployment .
[40]
3D TEE imaging’s role is pivotal with MitraClip procedures [Figure 7], for depth perception as well as the
[41]
spatial orientation not well appreciated during fluoroscopic imaging .
Echo and fluoroscopic images are displayed simultaneously to facilitate orientation of catheters and device
positioning. Given the great utility of 3D TEE in the assessment of patients with multiple valve orifices or
complex or multiple regurgitant jets, its advantages over traditional 2D TEE are self-evident when evaluating
[42]
patients after MitraClip [Figure 8] .