Page 129 - Read Online
P. 129
Calvo et al. Omega-3 fatty acids in cardiovascular health
membrane of erythrocytes leads to a decrease in concentrations due to its effect in NCX activity in the cell
the negative charge of the membrane, with reduced membrane. [112] In addition, it has been demonstrated
phospholipid fluidity, activation of the synthesis of that the Na /K ATPase activation modulates the
+
+
proinflammatory eicosanoids, and increased sensitivity function of L-type Ca channels, which causes
2+
of arterial smooth muscle cells to vasoconstrictive a greater release of calcium by the sarcoplasmic
effects. [103,104] reticulum and higher intracellular Ca gradients during
2+
systole, increasing contraction strength. [113]
Myocardial function
Reports from different human and animal models have Cardiac arrhythmia
demonstrated that n-3 PUFAs improve left ventricular Several studies have reported an association between
inotropic function, without causing hypertrophy n-3 PUFA intake and a lower risk of CVD-related
or increase in blood pressure. [105] The underlying death, specifically from ischemic events, where the
mechanism involves an increase in the activity of myosin myocardium is more prone to suffer irregularities in its
ATPase and Na /K ATPase, and the expression of electric activity that can lead to sudden death. [114,115]
+
+
Ca ATPase in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, which are
2+
associated with positive inotropism, and maintenance Myocardial cells at the border of the ischemic zone
of intra-sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium concentration have a relatively depolarized resting potential and can
and the sodium calcium exchanger (NCX). [106,107] potentially generate ventricular fibrillation because of
Furthermore, an indirect effect is achieved through how easily they can be excited. [114] Because of this, an
an increase in ventricular efficiency, which is defined elevation in n-3 PUFAs stabilizes the high excitability
as the production of the highest ejection volume with of these partially depolarized cells in the ischemic
the lowest possible oxygen consumption, and the myocardium. This prevents spontaneous or premature
decrease in blood pressure. [108] This is possible due depolarization, [116] resulting in a longer refractory
to the incorporation of DHA in the cell membrane, [109] period and an increase in the voltage needed for the
influencing the eicosanoids mechanism and cellular depolarization. [117-120] More specifically, n-3
modulating cellular Ca and its signaling pathways. [110] PUFAs can inhibit voltage-dependent Na , K and
2+
+
+
On the other hand, it has also been attributed to the Ca channels, as well as Na /Ca exchangers and
2+
2+
+
+
shortening in the monophasic action potential due to Ca -activated K channels. [121] Consequently, these
2+
the suppression of ATP-dependent K channels in the changes lower membrane excitability, [122] translating to
+
sarcolemma. [111] a net membrane-stabilizing effect. [116,123]
Another proposed mechanism is the increase in the Finally, an antiarrhythmic mechanism has been
Na /K + ATPase activity, which boosts Na implicated in the role that n-3 PUFAs play in autonomic
+
+
concentrations, diminishing the intracellular Ca control, by increasing the vagal tone. [124,125] Recent
2+
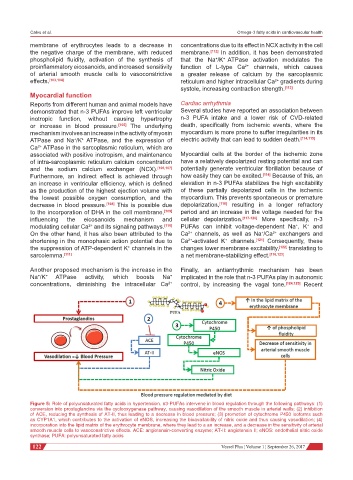
Figure 5: Role of polyunsaturated fatty acids in hypertension. n3-PUFAs intervene in blood regulation through the following pathways: (1)
conversion into prostaglandins via the cyclooxygenase pathway, causing vasodilation of the smooth muscle in arterial walls; (2) inhibition
of ACE, reducing the synthesis of AT-II, thus leading to a decrease in blood pressure; (3) promotion of cytochrome P450 isoforms such
as CYP1A1, which contributes to the activation of eNOS, increasing the bioavailability of nitric oxide and thus causing vasodilation; (4)
incorporation into the lipid matrix of the erythrocyte membrane, where they lead to a an increase, and a decrease in the sensitivity of arterial
smooth muscle cells to vasoconstrictive effects. ACE: angiotensin-converting enzyme; AT-II: angiotensin II; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide
synthase; PUFA: polyunsaturated fatty acids
122 Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ September 26, 2017