Page 130 - Read Online
P. 130
Calvo et al. Omega-3 fatty acids in cardiovascular health
evidence highlights that the effect n-3 PUFAs exert of transmembrane potentials during episodes of
on the electrophysiology of the ventricles and atria ischemia. [133]
relies on their favorable action on cell-cell connections
by modulating the expression and phosphorylation of A study on 211 patients with ST segment elevation
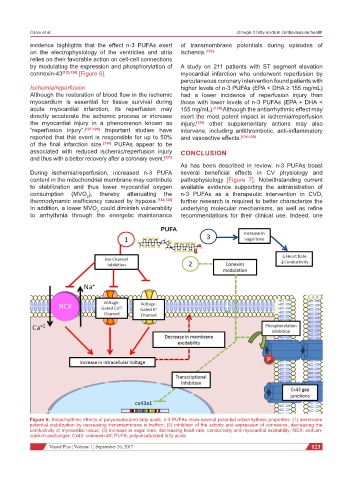
connexin-43 [125,126] [Figure 6]. myocardial infarction who underwent reperfusion by
percutaneous coronary intervention found patients with
Ischemia/reperfusion higher levels of n-3 PUFAs (EPA + DHA ≥ 155 mg/mL)
Although the restoration of blood flow in the ischemic had a lower incidence of reperfusion injury than
myocardium is essential for tissue survival during those with lower levels of n-3 PUFAs (EPA + DHA <
acute myocardial infarction, its reperfusion may 155 mg/mL). [134] Although the antiarrhythmic effect may
directly accelerate the ischemic process or increase exert the most potent impact in ischemia/reperfusion
the myocardial injury in a phenomenon known as injury, [135] other supplementary actions may also
“reperfusion injury”. [127-129] Important studies have intervene, including antithrombotic, anti-inflammatory
reported that this event is responsible for up to 50% and vasoactive effects. [136-138]
of the final infarction size. [130] PUFAs appear to be
associated with reduced ischemic/reperfusion injury CONCLUSION
and thus with a better recovery after a coronary event. [131]
As has been described in review, n-3 PUFAs boast
During ischemia/reperfusion, increased n-3 PUFA several beneficial effects in CV physiology and
content in the mitochondrial membrane may contribute pathophysiology [Figure 7]. Notwithstanding current
to stabilization and thus lower myocardial oxygen available evidence supporting the administration of
consumption (MVO ), thereby attenuating the n-3 PUFAs as a therapeutic intervention in CVD,
2
thermodynamic inefficiency caused by hypoxia. [132,133] further research is required to better characterize the
In addition, a lower MVO could diminish vulnerability underlying molecular mechanisms, as well as refine
2
to arrhythmia through the energetic maintenance recommendations for their clinical use. Indeed, one
Figure 6: Antiarrhythmic effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids. n-3 PUFAs show several potential antiarrhythmic properties: (1) membrane
potential stabilization by decreasing transmembrane io trafficn; (2) inhibition of the activity and expression of connexins, decreasing the
conductivity of myocardial tissue; (3) increase in vagal tone, decreasing heart rate, conductivity and myocardial excitability. NCX: sodium-
calcium exchanger; Cx43: connexin-43; PUFA: polyunsaturated fatty acids
Vessel Plus ¦ Volume 1 ¦ September 26, 2017 123