Page 165 - Read Online
P. 165
Page 34 of 43 Rao. Vessel Plus 2022;6:26 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1209.2021.93
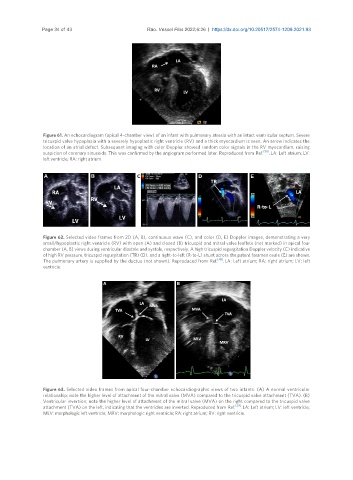
Figure 61. An echocardiogram (apical 4-chamber view) of an infant with pulmonary atresia with an intact ventricular septum. Severe
tricuspid valve hypoplasia with a severely hypoplastic right ventricle (RV) and a thick myocardium is seen. An arrow indicates the
location of an atrial defect. Subsequent imaging with color Doppler showed random color signals in the RV myocardium, raising
[50]
suspicion of coronary sinusoids. This was confirmed by the angiogram performed later. Reproduced from Ref. . LA: Left atrium; LV:
left ventricle; RA: right atrium.
Figure 62. Selected video frames from 2D (A, B), continuous wave (C), and color (D, E) Doppler images, demonstrating a very
small/hypoplastic right ventricle (RV) with open (A) and closed (B) tricuspid and mitral valve leaflets (not marked) in apical four
chamber (A, B) views during ventricular diastole and systole, respectively. A high tricuspid regurgitation Doppler velocity (C) indicative
of high RV pressure, tricuspid regurgitation (TR) (D), and a right-to-left (R-to-L) shunt across the patent foramen ovale (E) are shown.
The pulmonary artery is supplied by the ductus (not shown). Reproduced from Ref. [45] . LA: Left atrium; RA: right atrium; LV: left
ventricle.
Figure 63. Selected video frames from apical four-chamber echocardiographic views of two infants. (A) A normal ventricular
relationship; note the higher level of attachment of the mitral valve (MVA) compared to the tricuspid valve attachment (TVA). (B)
Ventricular inversion; note the higher level of attachment of the mitral valve (MVA) on the right compared to the tricuspid valve
attachment (TVA) on the left, indicating that the ventricles are inverted. Reproduced from Ref. [39] . LA: Left atrium; LV: left ventricle;
MLV: morphologic left ventricle; MRV: morphologic right ventricle; RA: right atrium; RV: right ventricle.