Page 119 - Read Online
P. 119
Page 18 of 25 Hao et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 39 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2025.48
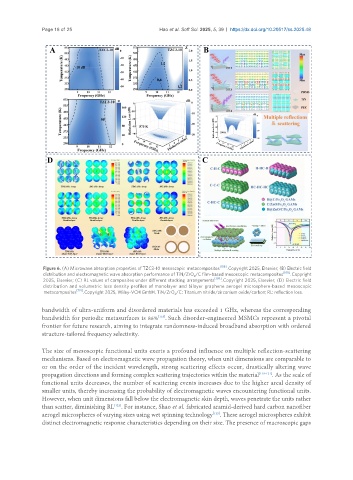
Figure 6. (A) Microwave absorption properties of TZC3-10 mesoscopic metacomposites [108] . Copyright 2025, Elsevier; (B) Electric field
distribution and electromagnetic wave absorption performance of TiN/ZrO /C film-based mesoscopic metacomposites [108] . Copyright
2
[109]
2025, Elsevier; (C) RL values of composites under different stacking arrangements . Copyright 2025, Elsevier; (D) Electric field
distribution and volumetric loss density profiles of monolayer and bilayer graphene aerogel microsphere-based mesoscopic
[114]
metacomposites . Copyright 2025, Wiley-VCH GmbH. TiN/ZrO /C: Titanium nitride/zirconium oxide/carbon; RL: reflection loss.
2
bandwidth of ultra-uniform and disordered materials has exceeded 1 GHz, whereas the corresponding
bandwidth for periodic metasurfaces is 86% . Such disorder-engineered MSMCs represent a pivotal
[118]
frontier for future research, aiming to integrate randomness-induced broadband absorption with ordered
structure-tailored frequency selectivity.
The size of mesoscopic functional units exerts a profound influence on multiple reflection-scattering
mechanisms. Based on electromagnetic wave propagation theory, when unit dimensions are comparable to
or on the order of the incident wavelength, strong scattering effects occur, drastically altering wave
propagation directions and forming complex scattering trajectories within the material [119-121] . As the scale of
functional units decreases, the number of scattering events increases due to the higher areal density of
smaller units, thereby increasing the probability of electromagnetic waves encountering functional units.
However, when unit dimensions fall below the electromagnetic skin depth, waves penetrate the units rather
than scatter, diminishing RL . For instance, Shao et al. fabricated aramid-derived hard carbon nanofiber
[122]
[123]
aerogel microspheres of varying sizes using wet spinning technology . These aerogel microspheres exhibit
distinct electromagnetic response characteristics depending on their size. The presence of macroscopic gaps