Page 117 - Read Online
P. 117
Page 16 of 25 Hao et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 39 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2025.48
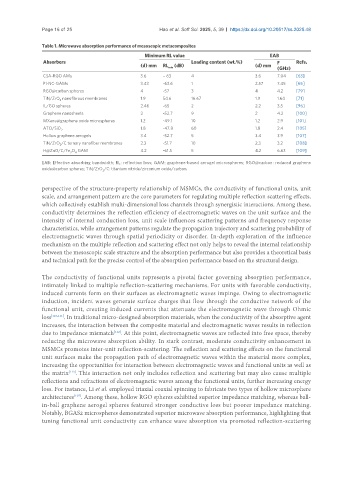
Table 1. Microwave absorption performance of mesoscopic metacomposites
Minimum RL value EAB
Absorbers Loading content (wt.%) F Refs.
(d) mm RL (dB) (d) mm (GHz)
min
CSA-RGO AMs 3.6 − 63 4 3.6 7.04 [63]
PI-NC-GAMs 3.43 -63.6 1 2.57 7.45 [65]
RGO@carbon spheres 4 -57 3 4 4.2 [79]
TiN/ZrO nanofibrous membranes 1.9 54.6 16.67 1.9 1.64 [71]
2
IL/GO spheres 2.46 -65 2 2.2 3.5 [96]
Graphene nanosheets 2 -52.7 9 2 4.2 [100]
MXene@graphene oxide microspheres 1.2 -49.1 10 1.2 2.9 [101]
ATO/SiO 1.8 -47.8 60 1.8 2.4 [105]
2
Hollow graphene aerogels 3.4 -52.7 5 3.4 3.9 [107]
TiN/ZrO /C ternary nanofiber membranes 2.3 -51.7 10 2.3 3.2 [108]
2
H@ZnO/C/Fe O GAM 4.2 -61.5 5 4.2 6.63 [109]
3
4
EAB: Effective absorbing bandwidth; RL: reflection loss; GAM: graphene-based aerogel microspheres; RGO@carbon: reduced graphene
oxide@carbon spheres; TiN/ZrO /C: titanium nitride/zirconium oxide/carbon.
2
perspective of the structure-property relationship of MSMCs, the conductivity of functional units, unit
scale, and arrangement pattern are the core parameters for regulating multiple reflection scattering effects,
which collectively establish multi-dimensional loss channels through synergistic interactions. Among these,
conductivity determines the reflection efficiency of electromagnetic waves on the unit surface and the
intensity of internal conduction loss, unit scale influences scattering patterns and frequency response
characteristics, while arrangement patterns regulate the propagation trajectory and scattering probability of
electromagnetic waves through spatial periodicity or disorder. In-depth exploration of the influence
mechanism on the multiple reflection and scattering effect not only helps to reveal the internal relationship
between the mesoscopic scale structure and the absorption performance but also provides a theoretical basis
and technical path for the precise control of the absorption performance based on the structural design.
The conductivity of functional units represents a pivotal factor governing absorption performance,
intimately linked to multiple reflection-scattering mechanisms. For units with favorable conductivity,
induced currents form on their surfaces as electromagnetic waves impinge. Owing to electromagnetic
induction, incident waves generate surface charges that flow through the conductive network of the
functional unit, creating induced currents that attenuate the electromagnetic wave through Ohmic
loss [110,111] . In traditional micro-designed absorption materials, when the conductivity of the absorptive agent
increases, the interaction between the composite material and electromagnetic waves results in reflection
due to impedance mismatch . At this point, electromagnetic waves are reflected into free space, thereby
[112]
reducing the microwave absorption ability. In stark contrast, moderate conductivity enhancement in
MSMCs promotes inter-unit reflection-scattering. The reflection and scattering effects on the functional
unit surfaces make the propagation path of electromagnetic waves within the material more complex,
increasing the opportunities for interaction between electromagnetic waves and functional units as well as
the matrix . This interaction not only includes reflection and scattering but may also cause multiple
[113]
reflections and refractions of electromagnetic waves among the functional units, further increasing energy
loss. For instance, Li et al. employed triaxial coaxial spinning to fabricate two types of hollow microsphere
architectures . Among these, hollow RGO spheres exhibited superior impedance matching, whereas ball-
[107]
in-ball graphene aerogel spheres featured stronger conductive loss but poorer impedance matching.
Notably, BGAS2 microspheres demonstrated superior microwave absorption performance, highlighting that
tuning functional unit conductivity can enhance wave absorption via promoted reflection-scattering