Page 115 - Read Online
P. 115
Page 14 of 25 Hao et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 39 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2025.48
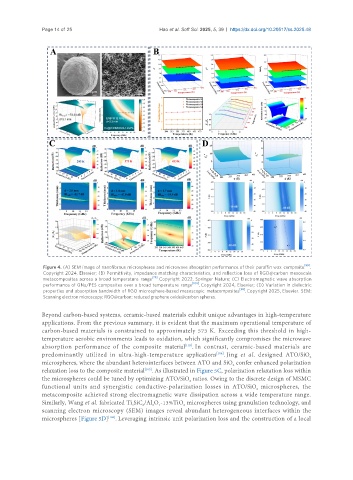
Figure 4. (A) SEM image of nanofibrous microspheres and microwave absorption performance of their paraffin wax composite [99] .
Copyright 2024, Elsevier; (B) Permittivity, impedance matching characteristics, and reflection loss of RGO@carbon mesoscale
metacomposites across a broad temperature range [79] . Copyright 2022, Springer Nature; (C) Electromagnetic wave absorption
[100]
performance of GNs/PES composites over a broad temperature range . Copyright 2024, Elsevier; (D) Variation in dielectric
[96]
properties and absorption bandwidth of RGO microsphere-based mesoscopic metacomposites . Copyright 2025, Elsevier. SEM:
Scanning electron microscopy; RGO@carbon: reduced graphene oxide@carbon spheres.
Beyond carbon-based systems, ceramic-based materials exhibit unique advantages in high-temperature
applications. From the previous summary, it is evident that the maximum operational temperature of
carbon-based materials is constrained to approximately 573 K. Exceeding this threshold in high-
temperature aerobic environments leads to oxidation, which significantly compromises the microwave
absorption performance of the composite material . In contrast, ceramic-based materials are
[103]
predominantly utilized in ultra-high-temperature applications . Jing et al. designed ATO/SiO
[104]
2
microspheres, where the abundant heterointerfaces between ATO and SiO confer enhanced polarization
2
relaxation loss to the composite material . As illustrated in Figure 5C, polarization relaxation loss within
[105]
the microspheres could be tuned by optimizing ATO/SiO ratios. Owing to the discrete design of MSMC
2
functional units and synergistic conductive-polarization losses in ATO/SiO microspheres, the
2
metacomposite achieved strong electromagnetic wave dissipation across a wide temperature range.
Similarly, Wang et al. fabricated Ti SiC /Al O -13%TiO microspheres using granulation technology, and
3
2
3
2
2
scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images reveal abundant heterogeneous interfaces within the
microspheres [Figure 5D] . Leveraging intrinsic unit polarization loss and the construction of a local
[106]