Page 112 - Read Online
P. 112
Hao et al. Soft Sci. 2025, 5, 39 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2025.48 Page 11 of 25
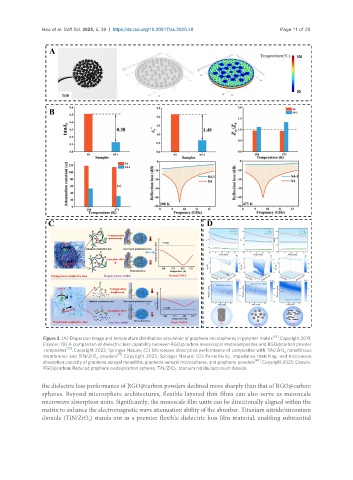
Figure 3. (A) Dispersion image and temperature distribution simulation of graphene microspheres in polymer matrix [92] . Copyright 2019,
Elsevier; (B) A comparison of dielectric loss capability between RGO@carbon mesoscopic metacomposites and RGO@carbon powder
composites [79] . Copyright 2022, Springer Nature; (C) Microwave absorption performance of composites with TiN/ZrO nanofibrous
2
membranes and TiN/ZrO powders [71] . Copyright 2023, Springer Nature; (D) Permittivity, impedance matching, and microwave
2
absorption capacity of graphene aerogel monoliths, graphene aerogel microspheres, and graphene powders [96] . Copyright 2025, Elsevier.
RGO@carbon: Reduced graphene oxide@carbon spheres; TiN/ZrO : titanium nitride/zirconium dioxide.
2
the dielectric loss performance of RGO@carbon powders declined more sharply than that of RGO@carbon
spheres. Beyond microsphere architectures, flexible layered thin films can also serve as mesoscale
microwave absorption units. Significantly, the mesoscale film units can be directionally aligned within the
matrix to enhance the electromagnetic wave attenuation ability of the absorber. Titanium nitride/zirconium
dioxide (TiN/ZrO ) stands out as a premier flexible dielectric loss film material, enabling substantial
2