Page 90 - Read Online
P. 90
Page 10 of 20 Lu et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:36 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.29
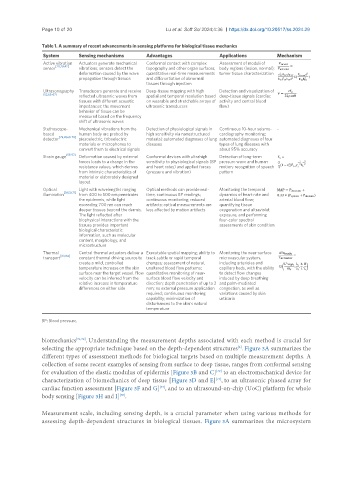
Table 1. A summary of recent advancements in sensing platforms for biological tissue mechanics
System Sensing mechanisms Advantages Applications Mechanism
Active vibration Actuators generate mechanical Conformal contact with complex Assessment of moduli of
[28,29,42]
sensor vibrations; sensors detect the topography and other organ surfaces; body regions (lesion, normal);
deformation caused by the wave quantitative real-time measurements tumor tissue characterization
propagation through tissues and differentiation of abnormal
tissues through injection
Ultrasonography Transducers generate and receive Deep-tissue mapping with high Detection and visualization of
[52,65-67]
reflected ultrasonic waves from spatial and temporal resolution based deep-tissue signals (cardiac
tissues with different acoustic on wearable and stretchable arrays of activity and central blood
impedances; the movement ultrasonic transducers flow)
behavior of tissue can be
measured based on the frequency
shift of ultrasonic waves
Stethoscope- Mechanical vibrations from the Detection of physiological signals in Continuous 10-hour seismo- -
based human body are probed by high sensitivity via nanostructured cardiography monitoring;
[29,41,68-70]
detector piezoelectric, triboelectric material; automated diagnoses of lung automated diagnoses of four
materials or microphones to diseases types of lung diseases with
convert them to electrical signals about 95% accuracy
[55-57]
Strain gauge Deformation caused by external Conformal devices with ultrahigh Detection of long-term
forces leads to a change in the sensitivity to physiological signals (BP pressure wave and human
resistance values, which derives and heart rates) and applied forces motion; recognition of speech
from intrinsic characteristics of (pressure and vibration) pattern
material or elaborately designed
layout
Optical Light with wavelengths ranging Optical methods can provide real- Monitoring the temporal
illumination [58,59,71] from 400 to 500 nm penetrates time, continuous BP readings; dynamics of heart rate and
the epidermis, while light continuous monitoring; reduced arterial blood flow;
exceeding 700 nm can reach artifacts: optical measurements are quantifying tissue
deeper tissues beyond the dermis. less affected by motion artifacts oxygenation and ultraviolet
The light reflected after exposure; and performing
biophysical interactions with the four-color spectral
tissues provides important assessments of skin condition
biological characteristic
information, such as molecular
content, morphology, and
microstructure
Thermal Central thermal actuators deliver a Executable spatial mapping; ability to Monitoring the near-surface
[63,64]
transport constant thermal driving source to track subtle or rapid temporal microvascular system,
create a mild, controlled changes; assessment of natural, including arterioles and
temperature increase on the skin unaltered blood flow patterns; capillary beds, with the ability
surface near the target vessel. Flow quantitative monitoring of near- to detect flow changes
velocity can be inferred from the surface blood flow velocity and induced by deep breathing
relative increase in temperature direction; depth penetration of up to 2 and palm-mediated
differences on either side mm; no external pressure application congestion, as well as
required; continuous monitoring variations caused by skin
capability; minimization of urticaria
disturbances to the skin’s natural
temperature
BP: Blood pressure.
biomechanics [71,72] . Understanding the measurement depths associated with each method is crucial for
[2]
selecting the appropriate technique based on the depth-dependent structures . Figure 3A summarizes the
different types of assessment methods for biological targets based on multiple measurement depths. A
collection of some recent examples of sensing from surface to deep tissue, ranges from conformal sensing
for evaluation of the elastic modulus of epidermis [Figure 3B and C] to an electromechanical device for
[29]
[73]
characterization of biomechanics of deep tissue [Figure 3D and E] , to an ultrasonic phased array for
[74]
cardiac function assessment [Figure 3F and G] , and to an ultrasound-on-chip (UoC) platform for whole
body sensing [Figure 3H and I] .
[65]
Measurement scale, including sensing depth, is a crucial parameter when using various methods for
assessing depth-dependent structures in biological tissues. Figure 3A summarizes the microsystem