Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Ma et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:26 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.20 Page 5 of 34
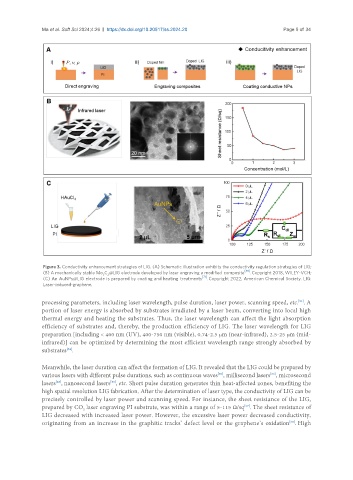
Figure 3. Conductivity enhancement strategies of LIG. (A) Schematic illustration exhibits the conductivity regulation strategies of LIG;
(B) A mechanically stable Mo C @LIG electrode developed by laser engraving a modified composite [69] . Copyright 2018, WILEY-VCH;
3
2
(C) An AuNPs@LIG electrode is prepared by coating and heating treatments [71] . Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society. LIG:
Laser-induced-graphene.
[51]
processing parameters, including laser wavelength, pulse duration, laser power, scanning speed, etc. . A
portion of laser energy is absorbed by substrates irradiated by a laser beam, converting into local high
thermal energy and heating the substrates. Thus, the laser wavelength can affect the light absorption
efficiency of substrates and, thereby, the production efficiency of LIG. The laser wavelength for LIG
preparation [including < 400 nm (UV), 400-750 nm (visible), 0.74-2.5 μm (near-infrared), 2.5-25 μm (mid-
infrared)] can be optimized by determining the most efficient wavelength range strongly absorbed by
substrates .
[64]
Meanwhile, the laser duration can affect the formation of LIG. It revealed that the LIG could be prepared by
[65]
[66]
various lasers with different pulse durations, such as continuous waves , millisecond lasers , microsecond
lasers , nanosecond lasers , etc. Short pulse duration generates thin heat-affected zones, benefiting the
[35]
[23]
high spatial resolution LIG fabrication. After the determination of laser type, the conductivity of LIG can be
precisely controlled by laser power and scanning speed. For instance, the sheet resistance of the LIG,
[67]
prepared by CO laser engraving PI substrate, was within a range of 5-115 Ω/sq . The sheet resistance of
2
LIG decreased with increased laser power. However, the excessive laser power decreased conductivity,
[68]
originating from an increase in the graphitic tracks’ defect level or the graphene’s oxidation . High