Page 88 - Read Online
P. 88
Page 12 of 27 Wang et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:32 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.15
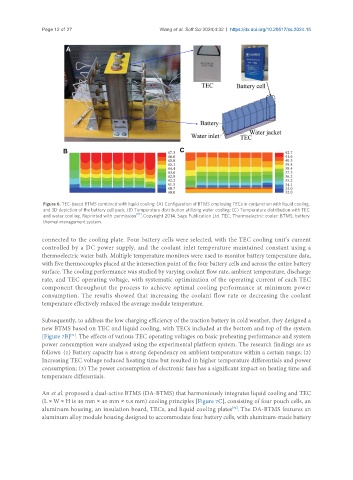
Figure 6. TEC-based BTMS combined with liquid cooling: (A) Configuration of BTMS employing TECs in conjunction with liquid cooling,
and 3D depiction of the battery cell pack; (B) Temperature distribution utilizing water cooling; (C) Temperature distribution with TEC
and water cooling. Reprinted with permission [37] . Copyright 2014, Sage Publication Ltd. TEC: Thermoelectric cooler; BTMS: battery
thermal management system.
connected to the cooling plate. Four battery cells were selected, with the TEC cooling unit’s current
controlled by a DC power supply, and the coolant inlet temperature maintained constant using a
thermoelectric water bath. Multiple temperature monitors were used to monitor battery temperature data,
with five thermocouples placed at the intersection point of the four battery cells and across the entire battery
surface. The cooling performance was studied by varying coolant flow rate, ambient temperature, discharge
rate, and TEC operating voltage, with systematic optimization of the operating current of each TEC
component throughout the process to achieve optimal cooling performance at minimum power
consumption. The results showed that increasing the coolant flow rate or decreasing the coolant
temperature effectively reduced the average module temperature.
Subsequently, to address the low charging efficiency of the traction battery in cold weather, they designed a
new BTMS based on TEC and liquid cooling, with TECs included at the bottom and top of the system
[Figure 7B] . The effects of various TEC operating voltages on basic preheating performance and system
[71]
power consumption were analyzed using the experimental platform system. The research findings are as
follows: (1) Battery capacity has a strong dependency on ambient temperature within a certain range; (2)
Increasing TEC voltage reduced heating time but resulted in higher temperature differentials and power
consumption; (3) The power consumption of electronic fans has a significant impact on heating time and
temperature differentials.
An et al. proposed a dual-active BTMS (DA-BTMS) that harmoniously integrates liquid cooling and TEC
(L × W × H is 40 mm × 40 mm × 0.8 mm) cooling principles [Figure 7C], consisting of four pouch cells, an
aluminum housing, an insulation board, TECs, and liquid cooling plates . The DA-BTMS features an
[72]
aluminum alloy module housing designed to accommodate four battery cells, with aluminum-made battery