Page 91 - Read Online
P. 91
Wang et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:32 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.15 Page 15 of 27
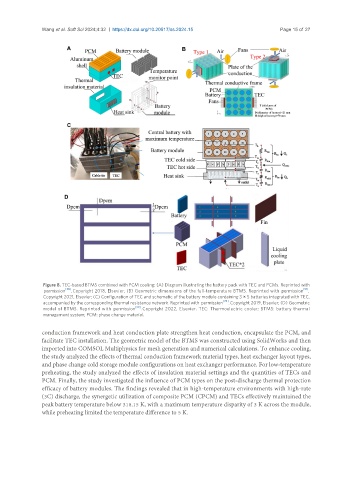
Figure 8. TEC-based BTMS combined with PCM cooling: (A) Diagram illustrating the battery pack with TEC and PCMs. Reprinted with
permission [38] . Copyright 2018, Elsevier; (B) Geometric dimensions of the full-temperature BTMS. Reprinted with permission [51] .
Copyright 2021, Elsevier; (C) Configuration of TEC and schematic of the battery module containing 3 × 5 batteries integrated with TEC,
accompanied by the corresponding thermal resistance network. Reprinted with permission [78] . Copyright 2019, Elsevier; (D) Geometric
[39]
model of BTMS. Reprinted with permission . Copyright 2022, Elsevier. TEC: Thermoelectric cooler; BTMS: battery thermal
management system; PCM: phase change material.
conduction framework and heat conduction plate strengthen heat conduction, encapsulate the PCM, and
facilitate TEC installation. The geometric model of the BTMS was constructed using SolidWorks and then
imported into COMSOL Multiphysics for mesh generation and numerical calculations. To enhance cooling,
the study analyzed the effects of thermal conduction framework material types, heat exchanger layout types,
and phase change cold storage module configurations on heat exchanger performance. For low-temperature
preheating, the study analyzed the effects of insulation material settings and the quantities of TECs and
PCM. Finally, the study investigated the influence of PCM types on the post-discharge thermal protection
efficacy of battery modules. The findings revealed that in high-temperature environments with high-rate
(3C) discharge, the synergetic utilization of composite PCM (CPCM) and TECs effectively maintained the
peak battery temperature below 318.15 K, with a maximum temperature disparity of 3 K across the module,
while preheating limited the temperature difference to 5 K.