Page 79 - Read Online
P. 79
Page 14 of 32 Zhao et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:18 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.04
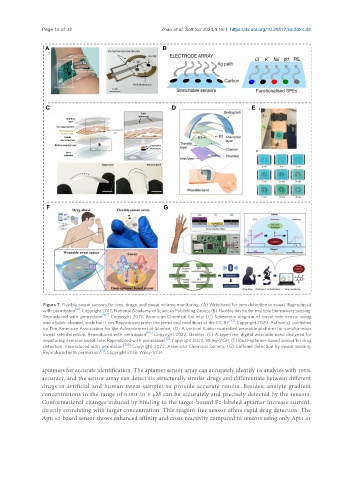
Figure 7. Flexible sweat sensors for ions, drugs, and sweat volume monitoring. (A) Wristband for ions detection in sweat. Reproduced
with permission [61] . Copyright 2017, National Academy of Sciences Publishing Group; (B) Flexible device for multiple biomarkers sensing.
Reproduced with permission [107] . Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society; (C) Schematic diagram of sweat rate sensor using
microfluidic channel, scale bar: 1 cm. Reproduced under the terms and conditions of the CC BY [47] . Copyright 2020, Author(s), published
by The American Association for the Advancement of Science; (D) A vertical fluidic-controlled wearable platform for simultaneous
sweat rate detection. Reproduced with permission [110] . Copyright 2022, Elsevier; (E) A tape-free, digital wearable band designed for
monitoring exercise sweat rate. Reproduced with permission [111] . Copyright 2023, Wiley-VCH; (F) Dual-aptamer-based sensor for drug
detection. Reproduced with permission [108] . Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society; (G) Caffeine detection by sweat sensing.
Reproduced with permission [18] . Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH.
aptamers for accurate identification. The aptamer sensor array can accurately identify 16 analytes with 100%
accuracy, and the sensor array can detect six structurally similar drugs and differentiate between different
drugs in artificial and human sweat samples to provide accurate results. Besides, analyte gradient
concentrations in the range of 0.001 to 5 μM can be accurately and precisely detected by the sensors.
Conformational changes induced by binding to the target-bound Fc-labeled aptamer increase current,
directly correlating with target concentration. This reagent-free sensor offers rapid drug detection. The
Apt1+2-based sensor shows enhanced affinity and cross-reactivity compared to sensors using only Apt1 or