Page 73 - Read Online
P. 73
Page 8 of 32 Zhao et al. Soft Sci 2024;4:18 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2024.04
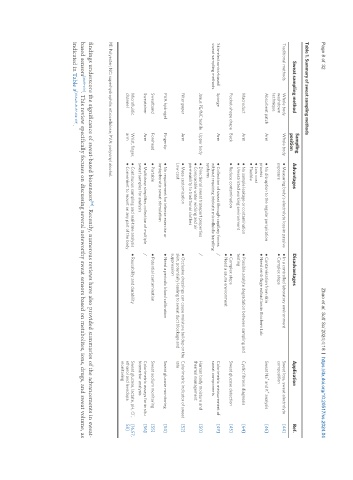
Table 1. Summary of sweat sampling methods
Sampling
Sweat sampling method Advantages Disadvantages Application Ref.
position
Traditional methods Whole body Whole body ● Measuring body’s electrolyte loss in passive ● In a controlled laboratory environment Sweat loss, sweat electrolyte [44]
washdown exposure ● Complex steps composition
technique
+
+
Absorbent patch Arm ● No disruption to the regular perspiration ● Contamination from skin Sweat Na and K analysis [46]
process ● Need centrifuge extraction in Biochem Lab
● Low cost
● Flexible
Macroduct Arm ● No sample leakage or contamination ● Possible analyte degradation between sampling and Cystic fibrosis diagnosis [64]
● Unrestricted working environment testing
Pocket-shape drape Back ● Reduce contamination ● Complex steps Sweat glucose detection [45]
● Need a sauna environment
Skin-electronics-based Sponge Arm ● Collection of sweat through capillary forces / Colorimetric measurement of [49]
sweat sampling methods without requiring intricate microfluidic handling sweat components
systems
Janus PE/NC textile Upper body ● Directional sweat transport properties / Human body moisture and [50]
● Comparable water wicking and air thermal management
permeability to traditional clothes
Filter paper Arm ● Mass customization ● Occlusive dressings can cause moisture buildup on the Colorimetric indicator of sweat [52]
Low cost skin, potentially leading to sweat duct blockage and rate
suppression
PVA hydrogel Fingertip ● No requirement for intense exercise or ● Need a periodic blood calibration Sweat glucose monitoring [54]
iontophoretic sweat stimulation
Sweatband Forehead ● Portable ● Potential contamination Sweat sodium monitoring [55]
Sweatainer Arm ● Multidraw simplifies collection of multiple / Colorimetric assays for in situ [56]
sweat samples for analysis biomarker analysis
-
Microfluidic Wrist, finger, ● Continuous sampling and real-time analysis ● Reusability and durability Sweat glucose, lactate, pH, Cl , [16,57,
channel arm ● Convenient to mount on any part of the body ethanol and levodopa 58]
monitoring
PE: Polyester; NC: superhydrophilic nitrocellulose; PVA: polyvinyl alcohol.
findings underscore the significance of sweat-based biosensors . Recently, numerous reviews have also provided summaries of the advancements in sweat-
[98]
based sensors [28,99-103] . This review specifically focuses on discussing several noteworthy sweat sensors based on metabolites, ions, drugs, and sweat volume, as
indicated in Table 3 [18,54,61,81,97,104-109] .