Page 12 - Read Online
P. 12
Xiao et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:11 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.03 Page 9 of 26
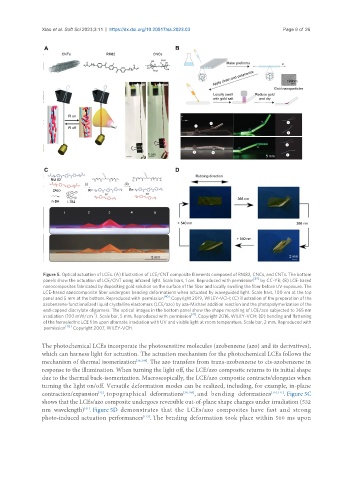
Figure 5. Optical actuation of LCEs. (A) Illustration of LCE/CNT composite filaments composed of RM82, CNCs, and CNTs. The bottom
panels show the actuation of LCE/CNT using infrared light. Scale bars, 1 cm. Reproduced with permission [92] by CC-YB; (B) LCE-based
nanocomposites fabricated by depositing gold solution on the surface of the fiber and locally swelling the fiber before UV exposure. The
LCE-based nanocomposite fiber undergoes bending deformations when actuated by waveguided light. Scale bars, 100 nm at the top
panel and 5 mm at the bottom. Reproduced with permission [40] . Copyright 2019, WILEY-VCH; (C) illustration of the preparation of the
azobenzene-functionalized liquid crystalline elastomers (LCE/azo) by aza-Michael addition reaction and the photopolymerization of the
end-capped diacrylate oligomers. The optical images in the bottom panel show the shape morphing of LCE/azo subjected to 365 nm
-2
irradiation (100 mW/cm ). Scale bar, 5 mm. Reproduced with permission [41] . Copyright 2016, WILEY-VCH; (D) bending and flattening
of the ferroelectric LCE film upon alternate irradiation with UV and visible light at room temperature. Scale bar, 2 mm. Reproduced with
permission [112] . Copyright 2007, WILEY-VCH.
The photochemical LCEs incorporate the photosensitive molecules (azobenzene (azo) and its derivatives),
which can harness light for actuation. The actuation mechanism for the photochemical LCEs follows the
mechanism of thermal isomerization [36,108] . The azo transfers from trans-azobenzene to cis-azobenzene in
response to the illumination. When turning the light off, the LCE/azo composite returns to its initial shape
due to the thermal back-isomerization. Macroscopically, the LCE/azo composite contracts/elongates when
turning the light on/off. Versatile deformation modes can be realized, including, for example, in-plane
contraction/expansion , topographical deformations [36,109] , and bending deformations [110,111] . Figure 5C
[32]
shows that the LCEs/azo composite undergoes reversible out-of-plane shape changes under irradiation (532
nm wavelength) . Figure 5D demonstrates that the LCEs/azo composites have fast and strong
[41]
[112]
photo-induced actuation performances . The bending deformation took place within 500 ms upon