Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Page 6 of 26 Xiao et al. Soft Sci 2023;3:11 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ss.2023.03
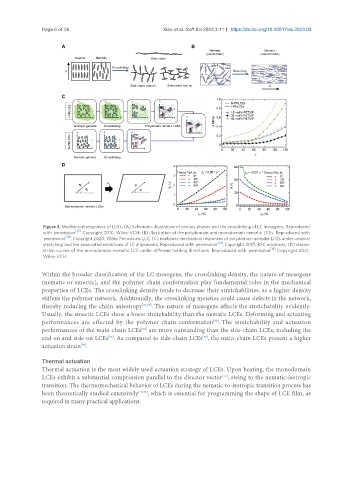
Figure 3. Mechanical responses of LCEs. (A) Schematic illustration of various phases and the crosslinking of LC mesogens. Reproduced
with permission [32] . Copyright 2010, Wiley-VCH; (B) illustration of the polydomain and monodomain nematic LCEs. Reproduced with
permission [38] . Copyright 2020, Wiley Periodicals LLC; (C) nonlinear mechanical responses of polydomain nematic LCEs under uniaxial
stretching and the associated evolutions of LC alignments. Reproduced with permission [39] . Copyright 2017, RSC advances; (D) stress-
strain curves of the monodomain nematic LCE under different loading directions. Reproduced with permission [16] . Copyright 2021,
Wiley-VCH.
Within the broader classification of the LC mesogens, the crosslinking density, the nature of mesogens
(nematic or smectic), and the polymer chain conformation play fundamental roles in the mechanical
properties of LCEs. The crosslinking density tends to decrease their stretchabilities, as a higher density
stiffens the polymer network. Additionally, the crosslinking moieties could cause defects in the network,
thereby reducing the chain anisotropy [71,72] . The nature of mesogens affects the stretchability evidently.
Usually, the smectic LCEs show a lower stretchability than the nematic LCEs. Deforming and actuating
performances are affected by the polymer chain conformation . The stretchability and actuation
[73]
performances of the main-chain LCEs are more outstanding than the side-chain LCEs, including the
[74]
end-on and side-on LCEs . As compared to side-chain LCEs , the main-chain LCEs present a higher
[75]
[76]
actuation strain .
[77]
Thermal actuation
Thermal actuation is the most widely used actuation strategy of LCEs. Upon heating, the monodomain
LCEs exhibit a substantial compression parallel to the director vector , owing to the nematic-isotropic
[17]
transition. The thermomechanical behavior of LCEs during the nematic-to-isotropic transition process has
been theoretically studied extensively [16,78] , which is essential for programming the shape of LCE film, as
required in many practical applications.