Page 248 - Read Online
P. 248
Rice et al. Minocycline in spinal cord injury
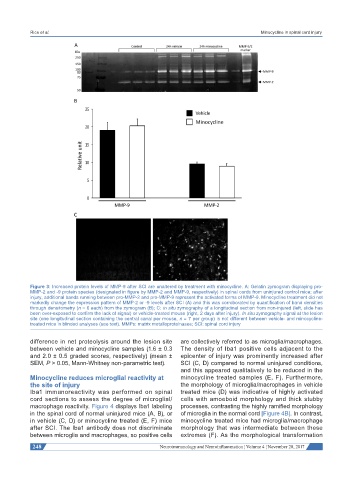
Figure 3: Increased protein levels of MMP-9 after SCI are unaltered by treatment with minocycline. A: Gelatin zymogram displaying pro-
MMP-2 and -9 protein species (designated in figure by MMP-2 and MMP-9, respectively) in spinal cords from uninjured control mice; after
injury, additional bands running between pro-MMP-2 and pro-MMP-9 represent the activated forms of MMP-9. Minocycline treatment did not
markedly change the expression pattern of MMP-2 or -9 levels after SCI (A) and this was corroborated by quantification of band densities
through densitometry (n = 6 each) from the zymogram (B); C: in situ zymography of a longitudinal section from non-injured (left, slide has
been over-exposed to confirm the lack of signal) or vehicle-treated mouse (right, 2 days after injury). In situ zymography signal at the lesion
site (one longitudinal section containing the central canal per mouse, n = 7 per group) is not different between vehicle- and minocycline-
treated mice in blinded analyses (see text). MMPs: matrix metalloproteinases; SCI: spinal cord injury
difference in net proteolysis around the lesion site are collectively referred to as microglia/macrophages.
between vehicle and minocycline samples (1.6 ± 0.3 The density of Iba1 positive cells adjacent to the
and 2.0 ± 0.5 graded scores, respectively) (mean ± epicenter of injury was prominently increased after
SEM, P > 0.05, Mann-Whitney non-parametric test). SCI (C, D) compared to normal uninjured conditions,
and this appeared qualitatively to be reduced in the
Minocycline reduces microglial reactivity at minocycline treated samples (E, F). Furthermore,
the site of injury the morphology of microglia/macrophages in vehicle
Iba1 immunoreactivity was performed on spinal treated mice (D) was indicative of highly activated
cord sections to assess the degree of microglial/ cells with amoeboid morphology and thick stubby
macrophage reactivity. Figure 4 displays Iba1 labeling processes, contrasting the highly ramified morphology
in the spinal cord of normal uninjured mice (A, B), or of microglia in the normal cord [Figure 4B]. In contrast,
in vehicle (C, D) or minocycline treated (E, F) mice minocycline treated mice had microglia/macrophage
after SCI. The Iba1 antibody does not discriminate morphology that was intermediate between these
between microglia and macrophages, so positive cells extremes (F). As the morphological transformation
248 Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ November 28, 2017