Page 250 - Read Online
P. 250
Rice et al. Minocycline in spinal cord injury
P < 0.05
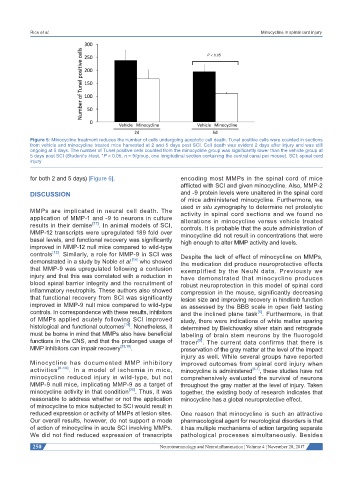
Figure 5: Minocycline treatment reduces the number of cells undergoing apoptotic cell death. Tunel positive cells were counted in sections
from vehicle and minocycline treated mice harvested at 2 and 5 days post SCI. Cell death was evident 2 days after injury and was still
ongoing at 5 days. The number of Tunel positive cells counted from the minocycline group was significantly lower than the vehicle group at
5 days post SCI (Student’s t-test, *P < 0.05, n = 9/group, one longitudinal section containing the central canal per mouse). SCI: spinal cord
injury
for both 2 and 5 days) [Figure 6]. encoding most MMPs in the spinal cord of mice
afflicted with SCI and given minocycline. Also, MMP-2
DISCUSSION and -9 protein levels were unaltered in the spinal cord
of mice administered minocycline. Furthermore, we
used in situ zymography to determine net proteolytic
MMPs are implicated in neural cell death. The activity in spinal cord sections and we found no
application of MMP-1 and -9 to neurons in culture alterations in minocycline versus vehicle treated
results in their demise [17] . In animal models of SCI, controls. It is probable that the acute administration of
MMP-12 transcripts were upregulated 189 fold over minocycline did not result in concentrations that were
basal levels, and functional recovery was significantly high enough to alter MMP activity and levels.
improved in MMP-12 null mice compared to wild-type
controls [12] . Similarly, a role for MMP-9 in SCI was Despite the lack of effect of minocycline on MMPs,
[14]
demonstrated in a study by Noble et al. who showed the medication did produce neuroprotective effects
that MMP-9 was upregulated following a contusion exemplified by the NeuN data. Previously we
injury and that this was correlated with a reduction in have demonstrated that minocycline produces
blood spinal barrier integrity and the recruitment of robust neuroprotection in this model of spinal cord
inflammatory neutrophils. These authors also showed compression in the mouse, significantly decreasing
that functional recovery from SCI was significantly lesion size and improving recovery in hindlimb function
improved in MMP-9 null mice compared to wild-type as assessed by the BBB scale in open field testing
controls. In correspondence with these results, inhibitors and the inclined plane task . Furthermore, in that
[5]
of MMPs applied acutely following SCI improved study, there were indications of white matter sparing
histological and functional outcomes [14] . Nonetheless, it determined by Bielchowsky silver stain and retrograde
must be borne in mind that MMPs also have beneficial labeling of brain stem neurons by the fluorogold
functions in the CNS, and that the prolonged usage of tracer . The current data confirms that there is
[5]
MMP inhibitors can impair recovery [18,19] . preservation of the gray matter at the level of the impact
injury as well. While several groups have reported
Minocycline has documented MMP inhibitory improved outcomes from spinal cord injury when
activities [8-10] . In a model of ischemia in mice, minocycline is administered [5-7] , these studies have not
minocycline reduced injury in wild-type, but not comprehensively evaluated the survival of neurons
MMP-9 null mice, implicating MMP-9 as a target of throughout the gray matter at the level of injury. Taken
minocycline activity in that condition [20] . Thus, it was together, the existing body of research indicates that
reasonable to address whether or not the application minocycline has a global neuroprotective effect.
of minocycline to mice subjected to SCI would result in
reduced expression or activity of MMPs at lesion sites. One reason that minocycline is such an attractive
Our overall results, however, do not support a mode pharmacological agent for neurological disorders is that
of action of minocycline in acute SCI involving MMPs. it has multiple mechanisms of action targeting separate
We did not find reduced expression of transcripts pathological processes simultaneously. Besides
250 Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ November 28, 2017