Page 138 - Read Online
P. 138
Chen et al. Characteristics of viral encephalitis with epilepsy
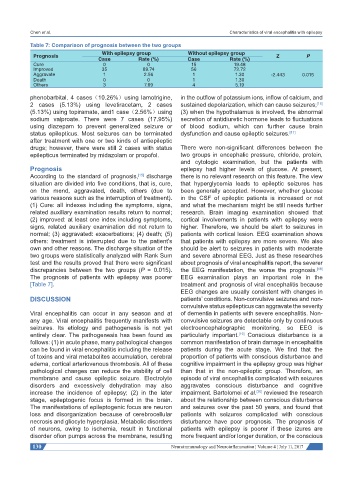
Table 7: Comparison of prognosis between the two groups
With epilepsy group Without epilepsy group
Prognosis Z P
Case Rate (%) Case Rate (%)
Cure 0 0 15 19.48
Improved 35 89.74 56 72.72
Aggravate 1 2.56 1 1.30 -2.443 0.015
Death 0 0 1 1.30
Others 3 7.69 4 5.19
phenobarbital, 4 cases(10.26%)using lamotrigine, in the outflow of potassium ions, inflow of calcium, and
2 cases (5.13%) using levetiracetam, 2 cases sustained depolarization, which can cause seizures;
[16]
(5.13%) using topiramate, and1 case(2.56%)using (3) when the hypothalamus is involved, the abnormal
sodium valproate. There were 7 cases (17.95%) secretion of antidiuretic hormone leads to fluctuations
using diazepam to prevent generalized seizure or of blood sodium, which can further cause brain
status epilepticus. Most seizures can be terminated dysfunction and cause epileptic seizures. [17]
after treatment with one or two kinds of antiepileptic
drugs; however, there were still 2 cases with status There were non-significant differences between the
epilepticus terminated by midazolam or propofol. two groups in encephalic pressure, chloride, protein,
and cytologic examination, but the patients with
Prognosis epilepsy had higher levels of glucose. At present,
According to the standard of prognosis, discharge there is no relevant research on this feature. The view
[15]
situation are divided into five conditions, that is, cure, that hyperglycemia leads to epileptic seizures has
on the mend, aggravated, death, others (due to been generally accepted. However, whether glucose
various reasons such as the interruption of treatment). in the CSF of epileptic patients is increased or not
(1) Cure: all indexes including the symptoms, signs, and what the mechanism might be still needs further
related auxiliary examination results return to normal; research. Brain imaging examination showed that
(2) improved: at least one index including symptoms, cortical involvements in patients with epilepsy were
signs, related auxiliary examination did not return to higher. Therefore, we should be alert to seizures in
normal; (3) aggravated: exacerbations; (4) death; (5) patients with cortical lesion. EEG examination shows
others: treatment is interrupted due to the patient’s that patients with epilepsy are more severe. We also
own and other reasons. The discharge situation of the should be alert to seizures in patients with moderate
two groups were statistically analyzed with Rank Sum and severe abnormal EEG. Just as these researches
test and the results proved that there were significant about prognosis of viral encephalitis report, the severer
discrepancies between the two groups (P = 0.015). the EEG manifestation, the worse the prognosis.
[18]
The prognosis of patients with epilepsy was poorer EEG examination plays an important role in the
[Table 7]. treatment and prognosis of viral encephalitis because
EEG changes are usually consistent with changes in
DISCUSSION patients’ conditions. Non-convulsive seizures and non-
convulsive status epilepticus can aggravate the severity
Viral encephalitis can occur in any season and at of dementia in patients with severe encephalitis. Non-
any age. Viral encephalitis frequently manifests with convulsive seizures are detectable only by continuous
seizures. Its etiology and pathogenesis is not yet electroencephalographic monitoring, so EEG is
entirely clear. The pathogenesis has been found as particularly important. Conscious disturbance is a
[19]
follows: (1) in acute phase, many pathological changes common manifestation of brain damage in encephalitis
can be found in viral encephalitis including the release patients during the acute stage. We find that the
of toxins and viral metabolites accumulation, cerebral proportion of patients with conscious disturbance and
edema, cortical arteriovenous thrombosis. All of these cognitive impairment in the epilepsy group was higher
pathological changes can reduce the stability of cell than that in the non-epileptic group. Therefore, an
membrane and cause epileptic seizure. Electrolyte episode of viral encephalitis complicated with seizures
disorders and excessively dehydration may also aggravates conscious disturbance and cognitive
increase the incidence of epilepsy; (2) in the later impairment. Bartolomei et al. reviewed the research
[20]
stage, epileptogenic focus is formed in the brain. about the relationship between conscious disturbance
The manifestations of epileptogenic focus are neuron and seizures over the past 50 years, and found that
loss and disorganization because of cerebrocellular patients with seizures complicated with conscious
necrosis and gliocyte hyperplasia. Metabolic disorders disturbance have poor prognosis. The prognosis of
of neurons, owing to ischemia, result in functional patients with epilepsy is poorer if these izures are
disorder ofion pumps across the membrane, resulting more frequent and/or longer duration, or the conscious
130 Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ July 11, 2017