Page 850 - Read Online
P. 850
Melillo et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:81 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.83 Page 7 of 17
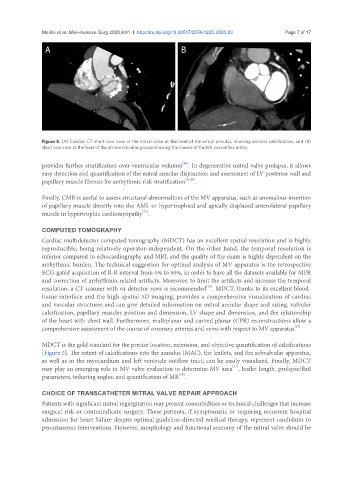
A B
Figure 5. (A) Cardiac CT short-axis view of the mitral valve at the level of the mitral annulus, showing annular calcification; and (B)
short axis view at the level of the atrioventricular groove showing the course of the left circumflex artery
[28]
provides further stratification over ventricular volumes . In degenerative mitral valve prolapse, it allows
easy detection and quantification of the mitral annular disjunction and assessment of LV posterior wall and
papillary muscle fibrosis for arrhythmic risk stratification [29,30] .
Finally, CMR is useful to assess structural abnormalities of the MV apparatus, such as anomalous insertion
of papillary muscle directly into the AML or hypertrophied and apically displaced anterolateral papillary
[31]
muscle in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy .
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
Cardiac multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) has an excellent spatial resolution and is highly
reproducible, being relatively operator-independent. On the other hand, the temporal resolution is
inferior compared to echocardiography and MRI, and the quality of the exam is highly dependent on the
arrhythmic burden. The technical suggestion for optimal analysis of MV apparatus is the retrospective
ECG-gated acquisition of R-R interval from 0% to 90%, in order to have all the datasets available for MPR
and correction of arrhythmia-related artifacts. Moreover, to limit the artifacts and increase the temporal
[32]
resolution, a CT scanner with 64 detector rows is recommended . MDCT, thanks to its excellent blood-
tissue interface and the high-spatial 3D imaging, provides a comprehensive visualization of cardiac
and vascular structures and can give detailed information on mitral annular shape and sizing, valvular
calcification, papillary muscles position and dimension, LV shape and dimension, and the relationship
of the heart with chest wall. Furthermore, multiplanar and curved planar (CPR) reconstructions allow a
[33]
comprehensive assessment of the course of coronary arteries and veins with respect to MV apparatus .
MDCT is the gold standard for the precise location, extension, and objective quantification of calcifications
[Figure 5]. The extent of calcifications into the annulus (MAC), the leaflets, and the subvalvular apparatus,
as well as in the myocardium and left ventricle outflow tract, can be easily visualized. Finally, MDCT
[34]
may play an emerging role in MV valve evaluation to determine MV area , leaflet length, prolapse/flail
[35]
parameters, tethering angles, and quantification of MR .
CHOICE OF TRANSCATHETER MITRAL VALVE REPAIR APPROACH
Patients with significant mitral regurgitation may present comorbidities or technical challenges that increase
surgical risk or contraindicate surgery. These patients, if symptomatic or requiring recurrent hospital
admission for heart failure despite optimal guideline-directed medical therapy, represent candidates to
percutaneous interventions. However, morphology and functional anatomy of the mitral valve should be